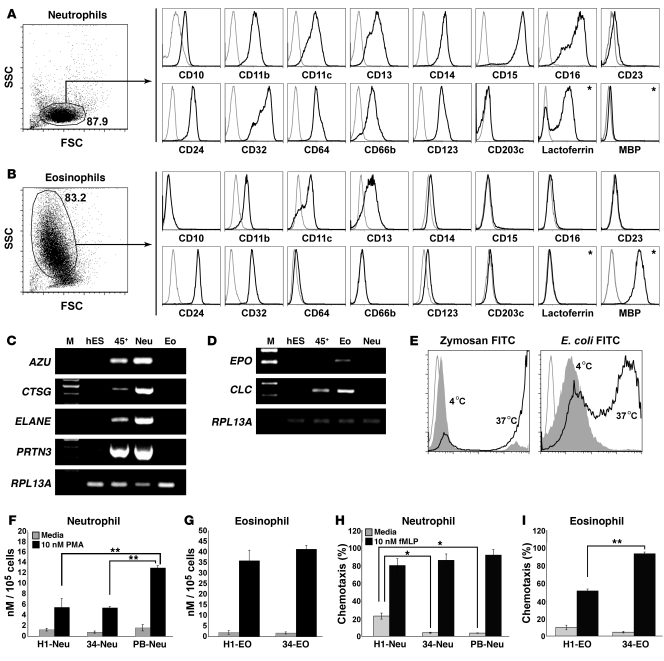
Figure 4. Phenotypic, molecular, and functional analysis of H1 hESC-derived eosinophils and neutrophils obtained from isolated CD235a/CD41a–CD45+ cells after 2 days expansion with GM-CSF.
FACS analysis of phenotype of hESC-derived neutrophils (A) and eosinophils (B). Plots show isotype control (gray) and specific antibody (black) histograms; asterisks indicate intracellular staining. Values within dot plots indicate the percentage of cells within the corresponding gate. A representative of 10 independent experiments is shown. Analysis of neutrophil and eosinophil-specific gene expression in hESC-derived neutrophils (C) and eosinophils (D) by RT-PCR. M, molecular weight markers; hES, undifferentiated hESCs; 45+, hESC-derived CD235a/CD41a–CD45+ cells isolated after 2 days expansion with GM-CSF; Neu, neutrophils; Eo is eosinophils. (E) Phagocytosis of zymozan and E. coli particles by hESC-derived neutrophils. Plots show histograms for isotype control (open gray) and cells incubated at 4°C (filled gray; nonspecific binding control) and 37°C (open black). (F) Superoxide production by hESC-derived (H1-Neu), somatic CD34+ cell–derived (34-Neu), and peripheral blood (PB-Neu) neutrophils in response to PMA. Results are mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate; **P < 0.01. (G) Superoxide production by hESC-derived (H1-EO) and somatic CD34+ cell–derived (34-EO) eosinophils in response to PMA. Results are mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate. (H) Chemotactic activity of hESC-derived, somatic CD34+ cell–derived, and peripheral blood neutrophils. Results are mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate; *P < 0.05. (I) Chemotactic activity of hESC-derived and somatic CD34+ cell–derived eosinophils. Results are mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments performed in triplicate; **P < 0.01.