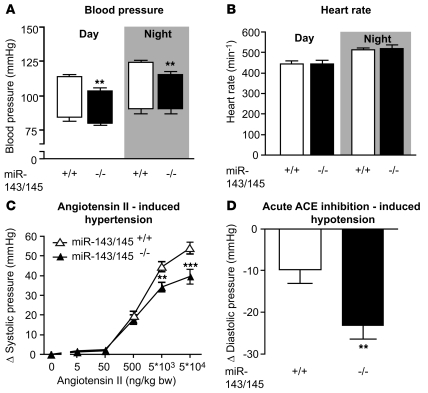
Figure 5. Hemodynamic measurements.
(A and B) In vivo blood pressure and heart rate measurements by telemetry. (A) Boxes show blood pressure amplitudes, with upper line representing systolic pressure and lower line, diastolic pressure; error bars indicate SEM. Systolic blood pressure was significantly reduced in miR-143/145–deficient mice during day- and nighttime periods (n = 6 WT and n = 7 KO, **P < 0.01), while diastolic pressure did not differ significantly between genotypes. (B) No difference in heart rate was observed between genotypes. (C) During isoflurane anesthesia, angiotensin II induced a larger increase in systolic blood pressure in WT (n = 12) than in KO mice (n = 13) (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (D) Acute inhibition of ACE by captopril lead to a greater decrease in diastolic pressure in miR-143/145–deficient animals (n = 11 WT and n = 13 KO, **P < 0.01). Error bars indicate ± SEM.