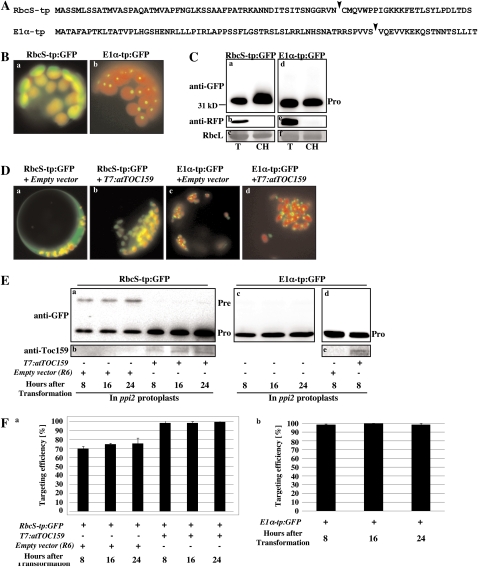
Figure 1.
Protein import of RbcS-tp:GFP and E1α-tp:GFP in wild-type and ppi2 mutant protoplasts. A, Sequences of RbcS-tp and E1α-tp. TP cleavage sites were predicted by TargetP (Emanuelsson et al., 2000) and indicated by arrowheads. B, Images of RbcS-tp:GFP and E1α-tp:GFP. Protoplasts from wild-type plants were transformed with RbcS-tp:GFP and E1α-tp:GFP and images were taken at 8 h after transformation. C, Western-blot analysis of RbcS-tp:GFP and E1α-tp:GFP. Protoplasts were transformed with RbcS-tp:GFP or E1α-tp:GFP together with RFP, and intact chloroplasts were purified using a percoll gradient. Protein extracts were prepared from intact purified chloroplasts and analyzed by western blotting using anti-GFP or anti-RFP antibodies. Total protoplast extracts were also included in the analysis. RFP was used as a representative of cytosolic proteins and the Rubisco large subunit stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue was used as a control for chloroplast purification. Pro, Processed forms; T, total protein extracts; CH, extracts from intact purified chloroplasts. D, Images of RbcS-tp:GFP and E1α-tp:GFP in ppi2 mutant protoplasts. Protoplasts from ppi2 plants were transformed with RbcS-tp:GFP or E1α-tp:GFP together with R6 (an empty expression vector) or T7:atTOC159. Images were taken 8 h after transformation. E, Protein import into ppi2 protoplasts. RbcS-tp:GFP and E1α-tp:GFP were transformed into ppi2 protoplasts together with R6 (empty expression vector) or T7:atTOC159, and protein extracts from transformed protoplasts were analyzed by western blotting using anti-GFP and anti-Toc159 antibodies at the indicated time points after transformation. Pre, Precursor forms. F, Quantification of protein imported into ppi2 chloroplasts. The import experiments were performed three times (Fig. 1E) and the data show the average import efficiencies at each time point (n = 3; error bar, sd). The import efficiency is expressed as the percentage of the amount of the processed form divided by the total amount of expressed protein.