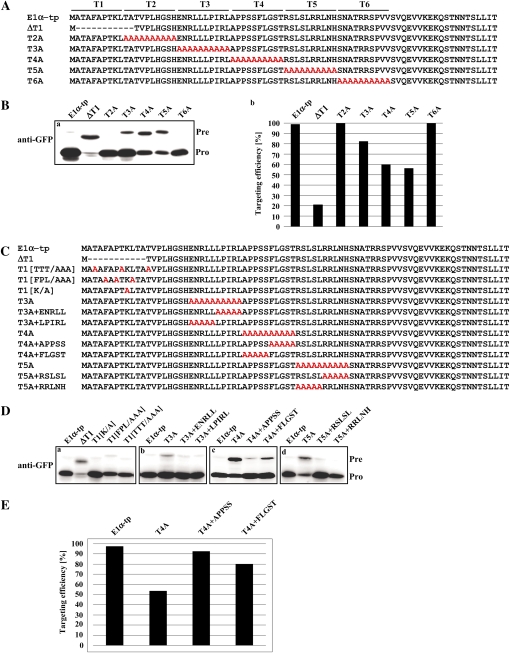
Figure 2.
Multiple sequence motifs in the E1α-tp play a critical role in protein import into chloroplasts. A, Sequence of Ala substitution or deletion mutants. E1α-tp was divided into six 10-amino acid segments, T1 to T6, and the amino acid residues in these segments were substituted with Alas to produce E1α[T2A] to E1α[T6A]. In addition, the T1 segment was deleted to produce E1α[ΔT1]. B, Import experiments for Ala substitution and deletion mutants. Protoplasts were transformed with these E1α-tp mutants and protein import efficiency of the mutants was examined by western-blot analysis using an anti-GFP antibody (a) and quantified (b). The import efficiency is expressed as the percentage of the amount of the processed form divided by the total amount of expressed protein. Pre, Precursor forms; Pro, processed forms. C, Sequences of the second set of Ala substitution mutants. As with the second set of mutants, the restoration mutants were generated such that the five amino acid residues of the first or second half of each T segment were restored to the original sequence on the background of the Ala substitution mutants E1α[T2A] to E1α[T6A]. For the T1 segment, three Thr residues, three hydrophobic amino acid residues (F, P, and L), or one Lys residue were substituted with the same number of Alas to produce E1α[TTT/AAA], E1α[FPL/AAA], or E1α[K/A], respectively. D, Import experiments with the second set of Ala substitution mutants. Protoplasts were transformed with these E1α-tp mutants and protein import efficiency of the mutants was assessed by western-blot analysis using anti-GFP antibody. E, Quantification of targeting efficiency of E1α-tp, T4A, T4A+APPSS, and T4A+FLGST. The import efficiency is expressed as the percentage of the amount of the processed form divided by the total amount of expressed protein.