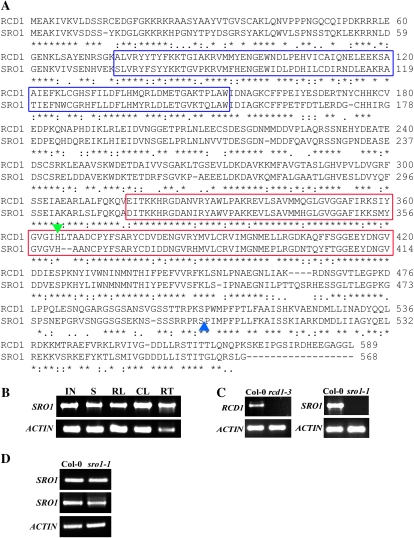
Figure 1.
RCD1 and SRO1 are similar proteins. A, Predicted amino acid sequences of the RCD1 and SRO1 proteins. SRO1 is 76% similar to RCD1. Asterisks, colons, and periods indicate identical, similar, and semiconserved amino acid residues, respectively. Hyphens correspond to gaps introduced to improve the alignment. The blue boxes mark the WWE domain, and the red boxes indicate the putative PARP catalytic domain. The insertion sites in rcd1-3 and sro1-1 are indicated by green (inverted) and blue (upright) triangles, respectively. B, SRO1 is expressed in all plant parts tested. RT-PCR was done using primers SRO1-F and SRO1-R to amplify SRO1 and Actin-F and Actin-R to amplify the actin control gene (Supplemental Table S1). IN, Inflorescence; S, 7-d-old seedlings; RL, rosette leaves; CL, cauline leaves; RT, roots. C, The T-DNA insertions in the mutant alleles disrupt gene expression. rcd1-3 and sro1-1 do not accumulate any detectable full-length transcript. RT-PCR was done using primers RCD1-F/RCD1-R and SRO1-F/SRO1-R, respectively. Col-0, Columbia. D, Transcription upstream and downstream of the T-DNA insertion site is seen in sro1-1. RT-PCR upstream (top panel; using primers SRO1-150F and SRO1-1360R) and downstream (middle panel; primers SRO1-1600F and SRO1-R) of the T-DNA insertion produces products.