Figure 6.
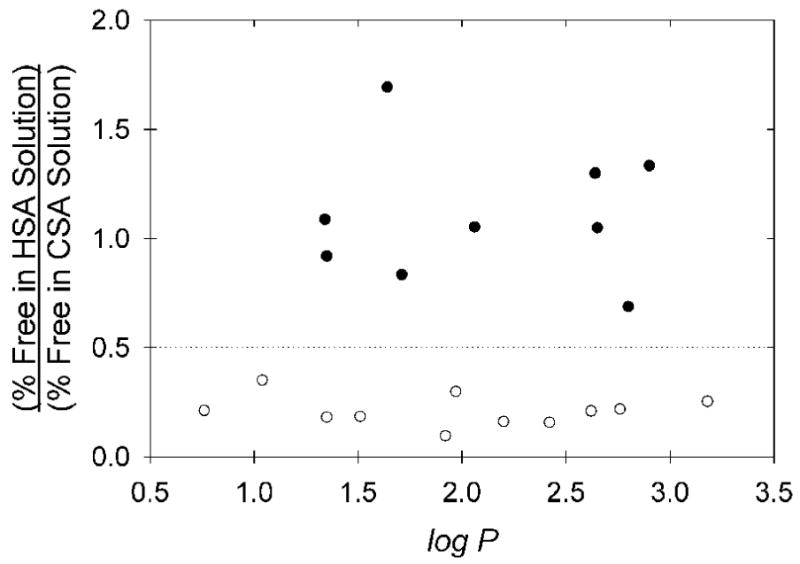
Ratio of measured HSA binding to CSA binding for the various copper(II) bis(thiosemicarbazone) radiopharmaceuticals, including values for the five pyruvaldehyde-derived “mixed” bis(thiosemicarbazone) copper(II) radiopharmaceuticals previously reported [4,5]. The dashed line (HSA/CSA Ratio = 0.5) is an apparent threshold above which binding to HSA is believed to be entirely non-specific, and largely approximated by the binding to CSA. The common structural feature of the eleven chelates below the dotted line, all appearing to bind with high affinity in the IIA site of HSA, is the presence of only methyl (-CH3) or -H substituents at the carbon atoms of the diimine backbone. The HSA/CSA binding ratios for these eleven chelates are less than from those of the nine chelates with bulkier substituents with P = 0.0001 (Mann-Whitney test).
