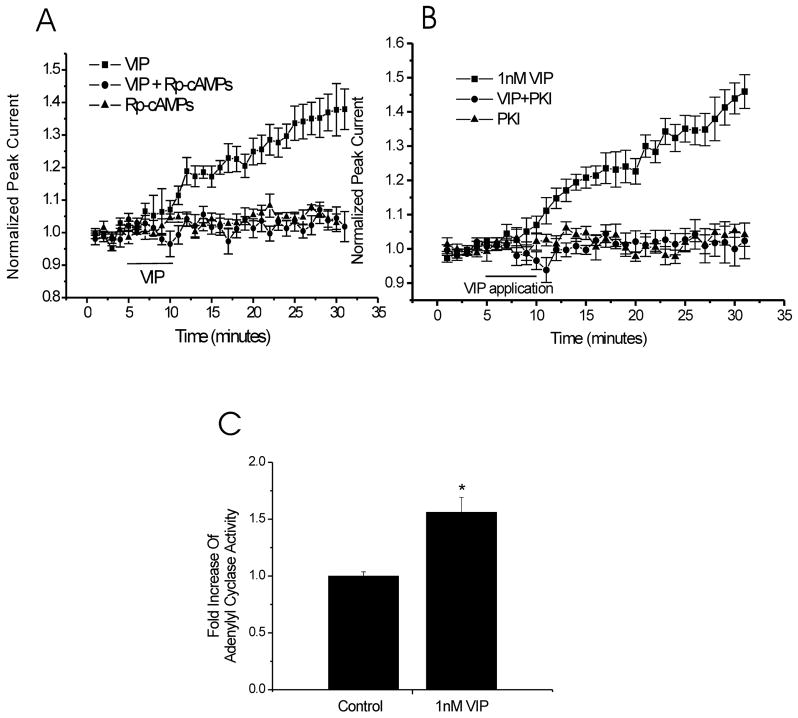
Figure 3. The cAMP/PKA signalling pathway is involved in VIP (1nM) response.
A. Intracellular administration 500μM Rp-cAMPs (a specific cAMP inhibitor) blocked the effect of VIP (4 ± 3%, n = 6, data obtained at 30 min of recording) and was similar to Rp-cAMPs alone (5 ± 2%, n = 5, data obtained at 30 min of recording). B. Addition of 0.3μM PKI14–22 (a specific PKA inhibitor) in all extracellular solutions blocked the potentiation of NMDA-evoked currents induced by VIP (1nM) (PKI14–22 plus VIP, 1 ± 4%, n = 6; VIP alone, 40 ± 5%, n = 6, data obtained at 30 min of recording). C. Adenylyl cyclase activity were compared between vesicle–treated and VIP (1nM)–treated brain tissue, VIP-treated tissue had a 1.56 ± 0.13-fold (n = 4) increase in AC activity (p < 0.05, unpaired t test).