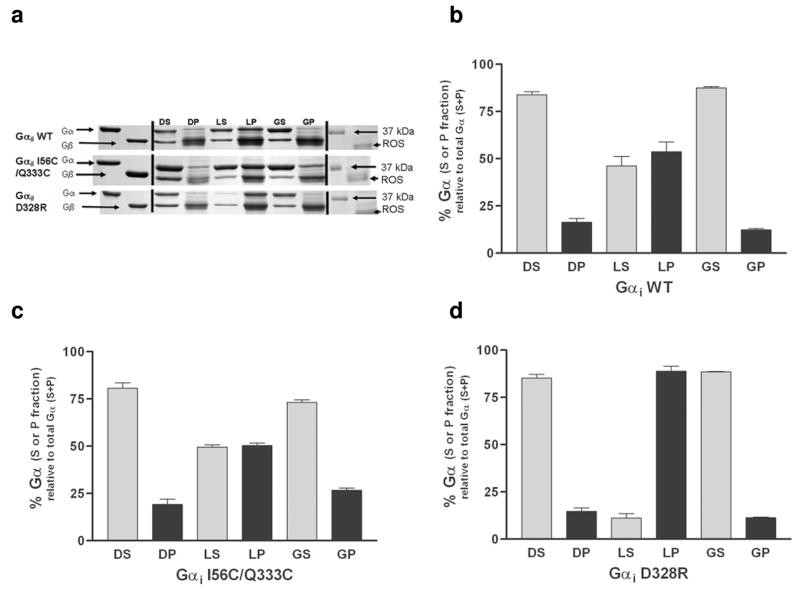
Figure 3.
Membrane localization and rhodopsin binding of the wild-type and mutant Gαi1 subunits. (a) Representative Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE analysis of wild-type (WT; top panel) I56C/Q333C (middle panel) and D328R (bottom panel) Gαi1 subunits reconstituted with excess Gβγ prior to binding to ROS in the dark, light, and after light activation followed by addition of GTPγS. DS, supernatant from dark sample; DP, pellet fraction from dark sample; LS, supernatant from light sample; LP, pellet from light sample; GS, supernatant from light and GTPγS activated sample; GP, pellet from light and GTPγS activated sample. (b) (c) and (d) and Quantitation of membrane binding. Each measurement is the average of three independent experiments. The D328R Gαi1 subunit showed a significant enhancement in binding to membrane fractions upon light activation as compared to either wild-type or I56C/Q333C Gαi1 subunits (**p = 0.0035 and p=0.0002, respectively).