Table 3.
Asymmetric Epoxidation of cis- and Trisubstituted Olefins by Ketone 3da
| entry | substrate | conv. (yield) (%)b | ee (%) | config.g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 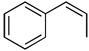 |
100c(60) | 85e | (−)-(1R,2S)3a |
| 2 | 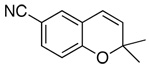 |
89d(87) | 84f | (+)-(3R,4R)3a |
| 3 | 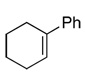 |
99c(89) | 80e | (−)-(S,S)2b,3c,d |
| 4 | 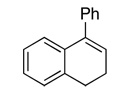 |
88d(56) | 90f | (+)-(1R, 2S)2b |
All reactions were carried out with substrate (0.2 mmol), ketone 3d (0.06 mmol for entry 1, 0.04 mmol for entries 2, 3, and 4), Oxone (0.32 mmol), and K2CO3 (1.344 mmol) in DME/DMM (3:1, v/v; 3.0 mL) and buffer (0.1 M K2CO3-AcOH in 4 × 10−4 M aqueous EDTA, pH 9.3; 2 mL); For entries 1, 3, and 4, the reaction was carried out at −10 °C for 4 h; For entry 2, the reaction was carried out at 0 °C for 12 h.
Isolated yield.
The conversion was determined by GC (B-DM column).
The conversion was determined by 1H NMR.
The ee was determined by chiral GC (B-DM column).
The ee was determined by chiral HPLC (Chiracel OD column).
The absolute configurations were determined by comparing the measured optical rotations and GC trace with reported ones.
