Figure 4.
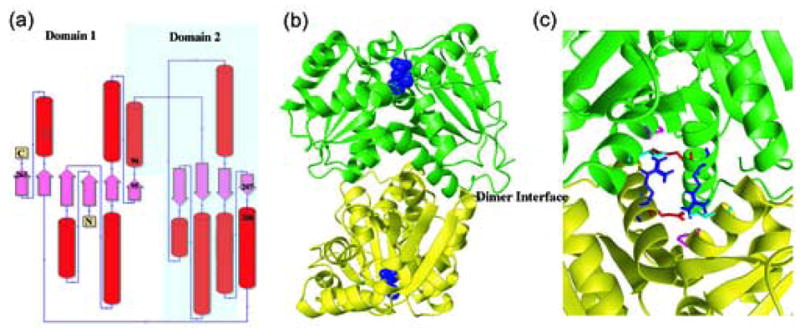
X-ray structures of RacE isozymes from Bacillus anthracis. (a) Topology diagram for the secondary structure elements of RacE1 and RacE2. Domain 1 is composed of residues 1-95 & 208-270 for RacE2, and 1-98 & 211-276 for RacE1. Domain 2 is composed of residues 96-207 for RacE2, and 99-210 for RacE1. (b) The homodimers are shown with the two chains colored green and yellow. The substrate D-glutamate is shown as space fill model (blue) and is located in the active site opposite the dimer interface (labeled). (c) Close-up view of the dimer interface of RacE2. The two monomers are shown in green and yellow. Amino acid R214 (blue), located in the middle of a helix in one monomer, is hydrogen bonded to the amino acids E215 (red), P99 (magenta) and T103 (cyan) in the other monomer. In RacE1, the corresponding residue R214 is replaced with Ile (I217). This alteration disrupts a total of 6 hydrogen bonds that stabilize the dimer interface between the two monomers.
