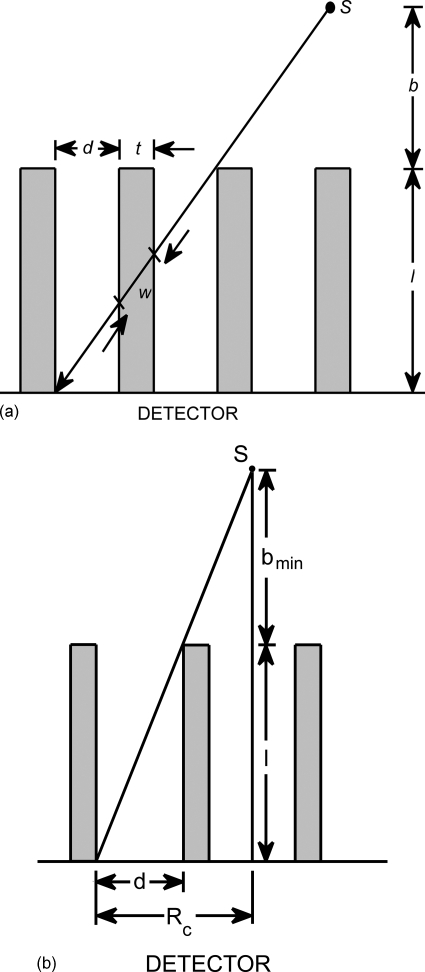
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of the side view of a collimator. Holes of length l and diameter d are separated by septa with thickness t. A point source S exists at distance b from the collimator surface. The shortest path an emitted gamma ray may travel through a septa is a distance w. (b) The general equations for a collimator’s sensitivity and resolution require that a source can be detected by more than one collimator hole. The distance bmin is the minimum source-to-collimator distance for which the classic equations still apply. At a distance less than bmin, a source is detected by only a single hole, and special considerations must be taken, especially regarding where the source is relative to the collimator septa.