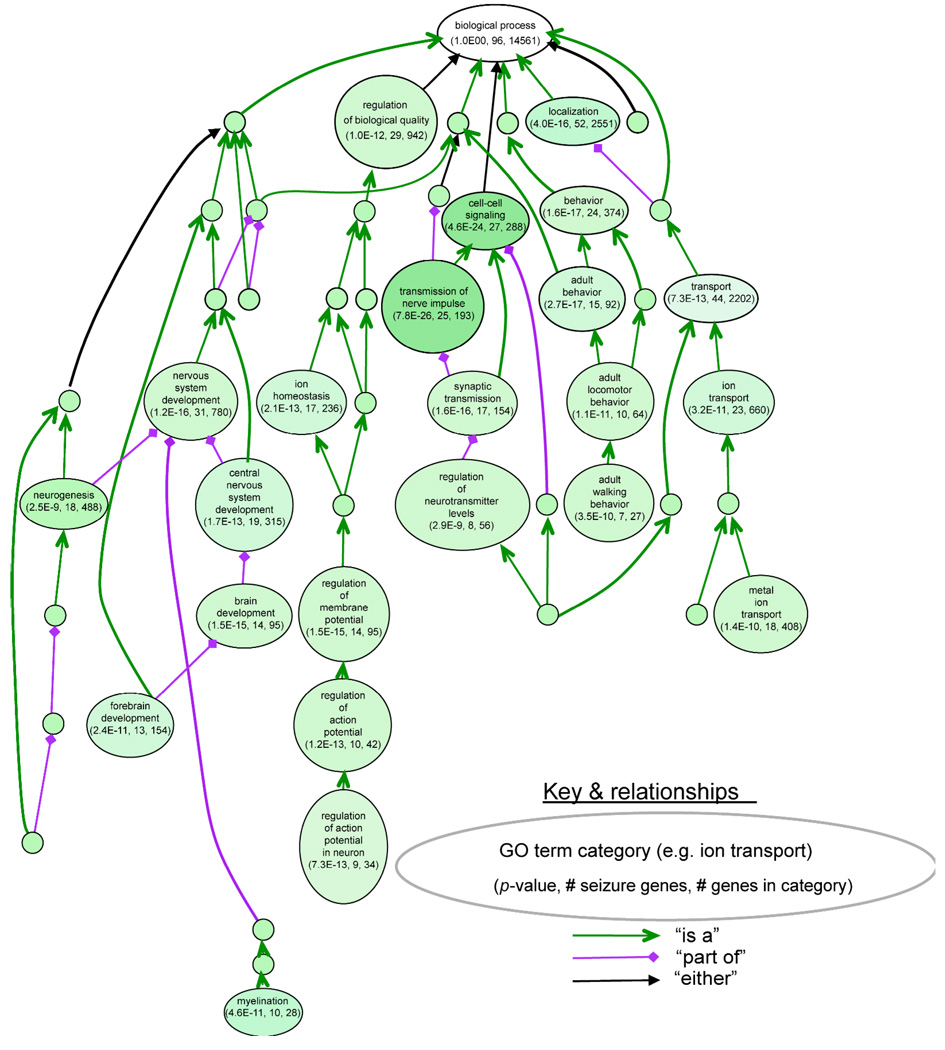
Figure 1. Classification of 101 mouse seizure genes using gene-ontology functional annotation.
This analysis was done using VLAD, a multipurpose prototype tool for visualizing and analyzing gene-ontology (GO) annotation data for sets of genes (http://proto.informatics.jax.org/prototypes/vlad-1.0.3/). Here VLAD was used to determine the overrepresentation of the 101 mouse seizure genes relative to total number of genes in each GO class for a biological process. Each large bubble shows a specific GO class, with the number of seizure genes in the class, the number of total genes in the class (from the Mouse Genome Informatics, MGI, database), and a P-value to estimate the relative overrepresentation of seizure genes in that class (see http://proto.informatics.jax.org/prototypes/vlad-1.0.3/ for methods). The arrows indicate the “parent-child” relationship of GO classes to one another; small, unlabelled bubbles are classes that were not significantly overrepresented. The existence of multiple larger bubbles containing significant class overrepresentations is indicative of multiple etiologies for seizure disorders in mice.