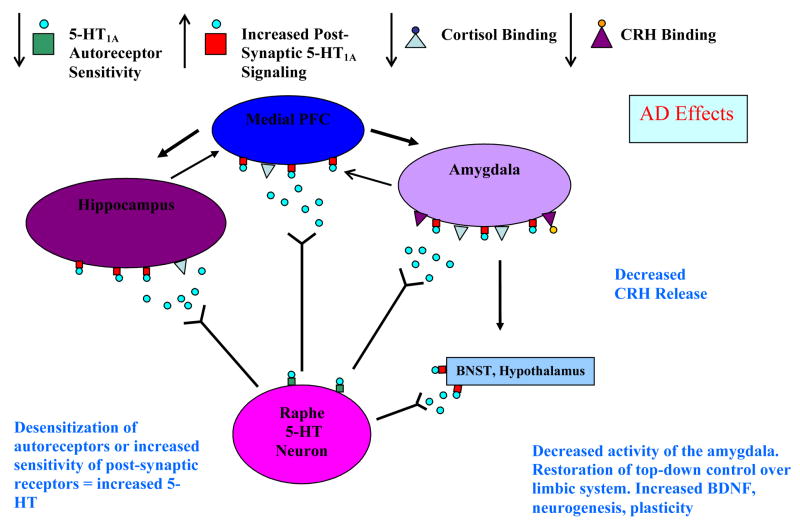
Figure 2. Simplified Model of 5-HT1A Receptor-Mediated Therapeutic Effects of AD.
AD are hypothesised to increase serotonergic signaling at the postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptor either by desensitizing the somatodendritic 5-HT1A receptor in the raphe, or by facilitating the activation of G proteins by the postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptor. Normalized signaling at the postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptor reduces cortisol and CRH release, restores endocrine function, and improves mood.