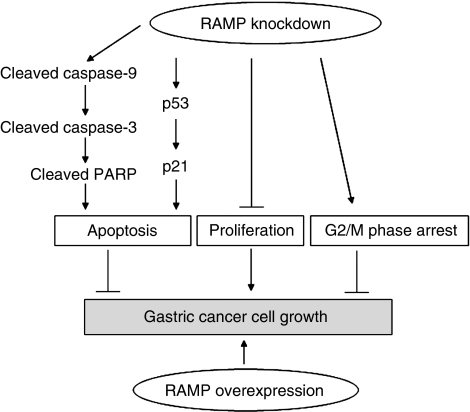
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram for the mechanisms of RAMP function in gastric cancer cells. Knockdown of RAMP inhibited gastric cancer cells growth, which was associated with several biological effects: (1) increasing the expression of cleaved caspase-9, caspase-3 and PARP, which in turn induced apoptosis; (2) inducing apoptosis caused by knockdown of RAMP was dependent on p53 and p21 pathways; (3) suppressing cell proliferation; (4) causing cell arrest in G2/M phase. On the other hand, overexpression of RAMP promoted growth capacity. Thus, RAMP may function as a novel oncogene in gastric cancer.