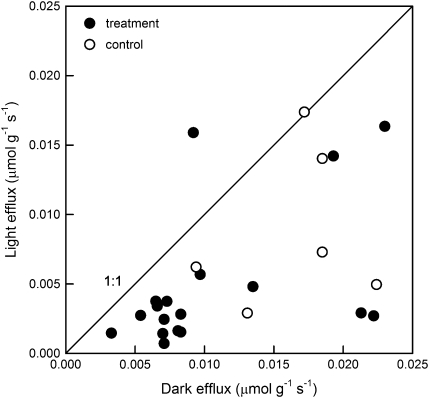
Fig. 3.
Woody tissue CO2 efflux of detached sycamore branches calculated from measurements made with an infrared gas analyser. Each branch was measured at two locations (lower, ∼25 cm from the cut end, and upper, ∼60 cm from the cut end). Measurements were made in sunlight after branches took up CO2-enriched water for at least 2 h, and repeated after the branches equilibrated in the dark for at least 2 h. Treatment branches (n=9) took up water enriched with 99 atom% 13CO2 at a concentration of 0.0116 mol l−1. Control branches (n=3) took up water enriched with 0.0114 mol l−1 CO2 at atmospheric isotope composition (∼1 atom% 13C). Light efflux was significantly different from dark efflux (t=3.731, P=<0.001, n=24), and light efflux was weakly correlated with dark efflux (light efflux=0.000621+0.430 (dark efflux), R2=0.23, P=0.011).