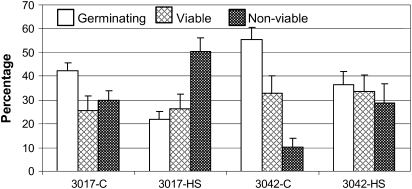
Fig. 1.
Effect of heat stress on tomato pollen quality. Tomato plants of cv. Hazera 3017 (heat sensitive) and cv. Hazera 3042 (heat tolerant) were exposed to a short-term HS (2 h at 43–45 °C). Pollen grains were collected from the heat-stressed (HS) plants of both cultivars (3017-HS, 3042-HS) and from control (C) plants (3017-C, 3042-C) 7, 6, 5, and 3 d after stress application. Mean values ±SE of the percentage germinating pollen grains, percentage viable pollen grains, and percentage non-viable pollen grains are presented. The mean values were calculated from the combined results of all tested developmental stages, derived from at least five biological replicates. The total number of pollen grains in both cultivars under control and HS conditions was similar and ranged between 38 and 50×103.