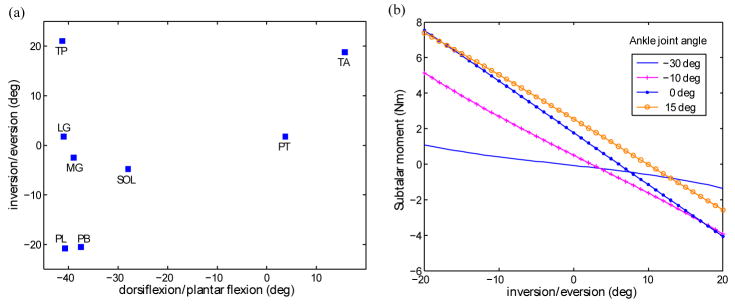
Fig. 2.
Model analysis. (a) The steady state output joint angles when each of eight muscles is fully activated. (b) An example of strong coupling and nonlinearity properties of the ankle-subtlar joint system. The subtalar joint moments generated by the maximum MG activation with respect to subtalar joint angle variations were calculated for four different ankle joint angles from −30° to 15°. The magnitudes and the direction of the subtalar joint moment depend on the ankle joint angle as well as the subtalar joint angle.