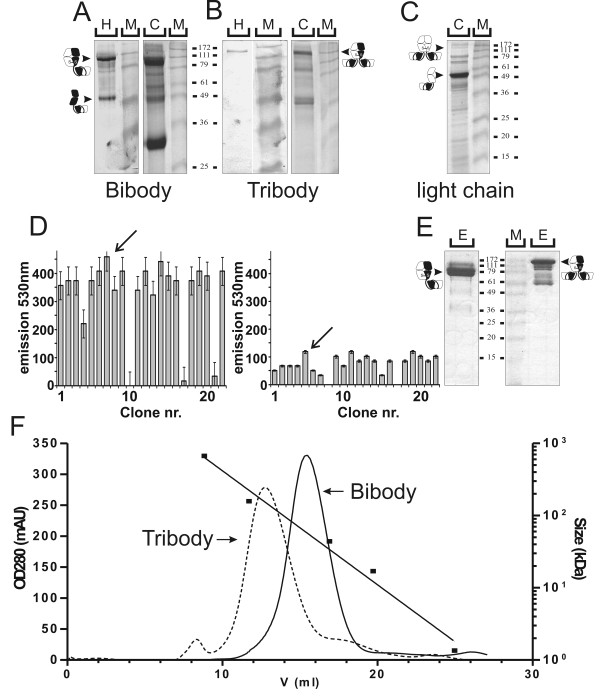
Figure 4.
Characterisation and purification of yeast produced PH1 bi- and tribody. A, B, 12.5% SDS-PAGE characterisation of culture supernatant from the PH1 bibody (A) or tribody (B) expressing P. pastoris cells. Left panels show S-protein-AP detected western blots of 100 μl samples. Right panels show Coomassie detection of 200 μl samples. C, Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel of 200 μl culture supernatant from PH1-scFv PH1 light chain expressing P. pastoris cells. Arrows and antibody chain symbols indicate the running height for PH1 derived proteins. M: relative molecular mass marker. D, S-tag assay for expression level screening of 22 Pichia pastoris bi- and tribody clones. Left graph shows results for the bibody, right graph for the tribody. Based on these results, bibody clone Pichia-Bi7 and tribody clone Pichia-Tri5 were selected for production. E, Coomassie stained 15% SDS-PAGE gel showing 1/500 samples from the IMAC elution fractions of PH1 bibody (left) and tribody (right) purified from ammonium precipitated Pichia supernatant. F, SEC purification of yeast produced PH1 bi- and tribody. UV 280 nm chromatogram of the P. pastoris produced PH1 bibody (solid line) and tribody (dotted line) purified on a Superdex 200 HR10/30 column. Arrows depict PH1 bibody and tribody peaks. Also indicated is the Bio-rad molecular mass standard run under similar conditions on the same column (black squares).