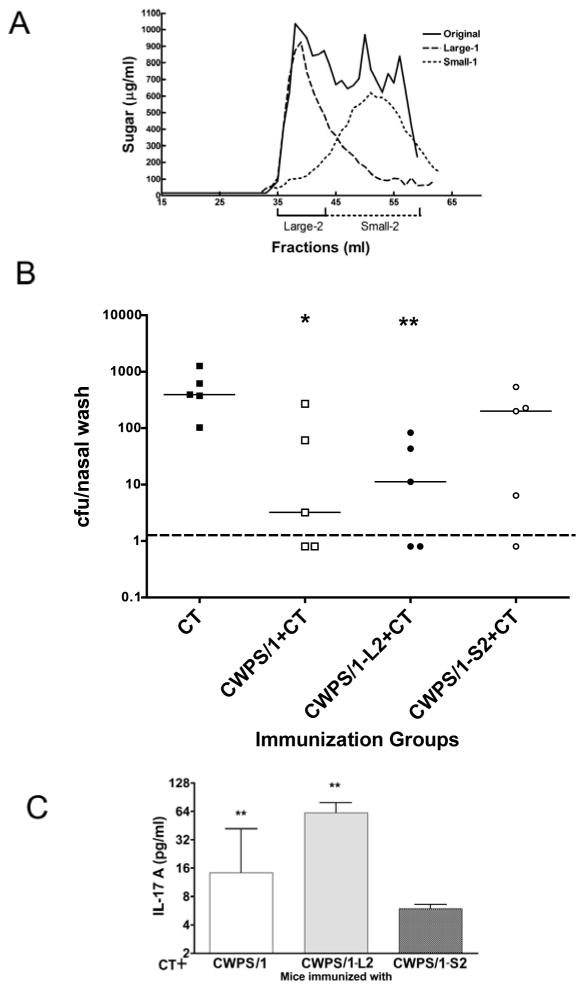
Figure 3. Molecular sieve fractionation of CWPS/1 and the effect of size on protection against NP colonization and priming for IL17A elicitation in vitro.
(A) CWPS/1 was size-fractionated on a 1×115 cm column of Sephacryl S300 with PBS as eluant. A 10-mg sample was applied, and the elution profile of 1-ml fractions determined by assay of sugar content. Fractions 35–43 were pooled as L1 and fractions 44–59 as S1. The pools were dialyzed vs water, concentrated by lyophilization, then separately refractionated. Fractions 35–43 of L1 were pooled as L2 and fractions 44–59 of S1 pooled as S2; these pools were dialyzed and lyophilized. (B) C57BL/6 mice (n=5 per group) were immunized with CT alone, or CT with CWPS/1, the large fraction of CWPS/1 (CWPS/1-L2) or the small fraction (CWPS/1-S2). Mice immunized with CWPS or CWPS/1-L2 were significantly protected against colonization compared to mice immunized with CT alone (P<0.05 and <0.01 respectively by Mann-Whitney U), whereas mice immunized with CWPS/1-S2 were not protected. (C) Whole blood from mice immunized with CWPS/1 or CWPS/1-L2 produce significantly more IL-17A in response to stimulation with killed whole-cell pneumococcal antigen (WCA) than from mice immunized with CWPS/1-S2 (*P=0.03 by Mann-Whitney U). Dashed line represents the lower limit of detection.