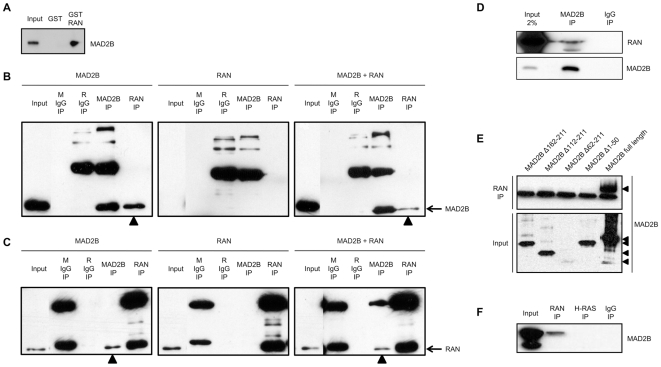
Figure 2. Co-immunoprecipitation of MAD2B and RAN proteins.
(A) U2OS cells expressing HA-MAD2B protein were lysed and probed for interaction with either GST-RAN or GST alone. Specific interaction between MAD2B and RAN was detected by western blot analysis using an anti-MAD2B antibody. (B, C) COS-1 cells were transiently transfected with MAD2B, RAN or both as indicated on top. Immunoprecipitations were performed with pre-mouse serum (M IgG), pre-rabbit serum (R IgG), anti-MAD2B and anti-RAN antibodies as indicated. Western blot analyses were performed with (B) an anti-MAD2B antibody, and (C) an anti-RAN-antibody. The positions of the immunoreactive MAD2B and RAN proteins are marked on the right. The (co-)immunoprecipitated MAD2B (B) and RAN (C) proteins are marked with arrowheads. The background bands represent immunoglobulin heavy and light chains, respectively. (D) Immunoprecipitations were carried out with an anti-MAD2B antibody and a control rabbit antibody (IgG) on HeLa cell lysates as indicated. Western blots analyses were performed with an anti-RAN (upper panel) and an anti-MAD2B (lower panel) antibody, respectively. (E) COS-1 cells were transiently transfected with FLAG-MAD2B protein and FLAG-tagged deletion constructs of MAD2B as indicated (see also Fig. 1). Upper panel: immunoprecipitations with an anti-RAN antibody, lower panel: input lysates. The background bands in the upper panel represent immunoglobulin light chains. Western blot analyses were performed with an anti-FLAG antibody. (F) COS-1 cells were transiently transfected with MAD2B and immunoprecipitations were performed with anti-RAN and anti-H-RAS antibodies, respectively. A pre-mouse serum (IgG) was included as a negative control. Western blot analysis was performed with an anti-MAD2B antibody.