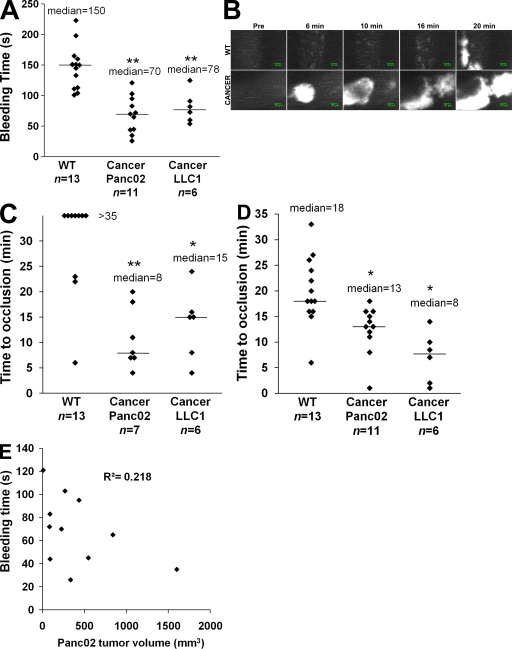
Figure 5.
Characterization of a thrombotic state in mice developing tumors. Kinetics of thrombosis in wild-type mice or in mice developing Panc02-derived (Cancer Panc02) or LLC1-derived (Cancer LLC1) tumors. (A) Bleeding times were determined in wild-type mice (n = 13 mice), mice developing a Panc02 tumor (n = 11 mice), or mice developing an LLC1 tumor (n = 6 mice). (B) Thrombus formation was studied after infusion of Alexa Fluor 660–conjugated anti-CD41 Fab fragment and Syto 62 in wild-type mice and in mice developing tumors. Injury was induced in mesenteric vessels by topical application of 10% FeCl3 for 5 min. Representative fluorescence images depicting the kinetics of thrombus formation of labeled platelet accumulation (white) on mesenteric arterioles (Pre, before injury). (C and D) Time to vessel occlusion reported in minutes for mesenteric arterioles (n = 13, 7, and 6 thrombi for WT, Cancer Panc02, and Cancer LLC1, respectively; C) and venules (n = 13, 11, and 6 thrombi for WT, Cancer Panc02, and Cancer LLC1, respectively; D). One injury was performed per mouse. (E) Bleeding times (in seconds) in function of the tumor volume (in mm3) in Panc02 tumor–bearing mice (n = 11). The linear coefficient of determination value is represented by R2. Horizontal bars in A, C, and D indicate median values. Experiments were independently performed at least six times (A–D) and 11 times (E). **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05.