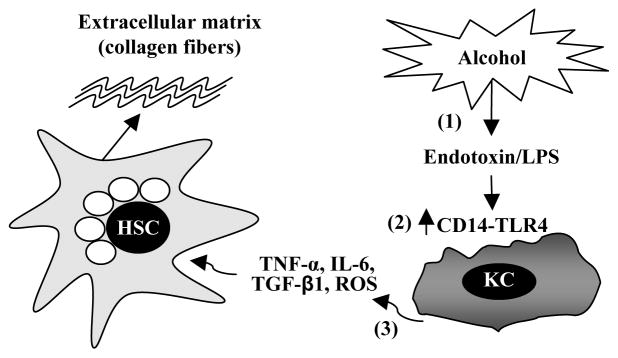
Figure 2. Alcohol amplifies the pro-fibrogenic effects of Kupffer cells.
Alcohol consumption permeabilizes the gut, resulting in elevated hepatic endotoxin levels, which is followed by activation of Kupffer cells. Activated Kupffer cells produce a variety of proinflammatory cytokines and inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, TGF-β1 and reactive oxygen species (ROS), which then activate HSCs, leading to production of extracellular matrix (collagen fibers) and liver fibrosis. Chronic alcohol consumption also increases the sensitivity of Kupffer cells to endotoxin via upregulation of CD14 expression.72–74