Figure 2.
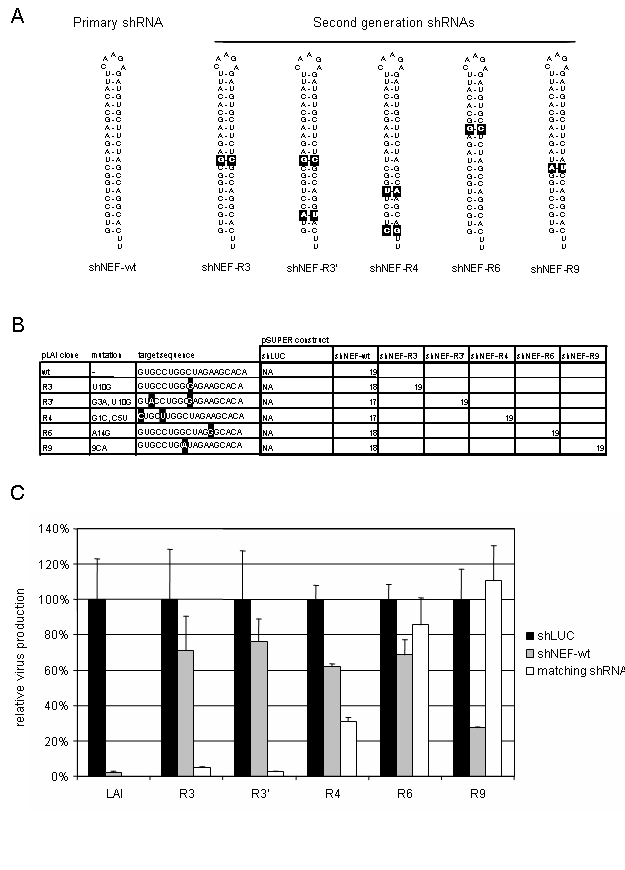
Counteracting HIV-1 escape with a second generation of shRNAs. (A) Hairpin structure of the shRNA molecules. Shown is the shNEF-wt and a second generation of shRNA variants that counteract escape mutants of HIV-1. Altered nucleotides are highlighted. (B) Molecular clones with sequence variation in the target were co-transfected with shRNA expressing constructs: either the shLUC control, the shNEF-wt or the matching shRNA variant. The number of basepair complementarity of the predicted siRNA and the target are shown. (C) Co-transfections were performed in 293T cells with 500 ng of pLAI molecular clone, 100 ng of pSUPER plasmid and 2.5 ng pRL as an internal control. Transfection was performed on 1.5 × 105 cells with lipofectamine-2000 according to the manufacturers instructions (Invitrogen). Two days post-transfection, CA-p24 was measured in the cell culture supernatant and Renilla activity measured in cell extract. The ratio between CA-p24 and internal control values yields the relative CA-p24 production, for all pLAI transfections the control shLUC were set at 100%. Black bars represent co-transfections with the control shLUC, transfections with shNEF-wt are shown in grey. The white bars represent co-transfections of the respective pLAI molecular clones with the matching pSUPER-shRNA counterpart.
