Figure 3.
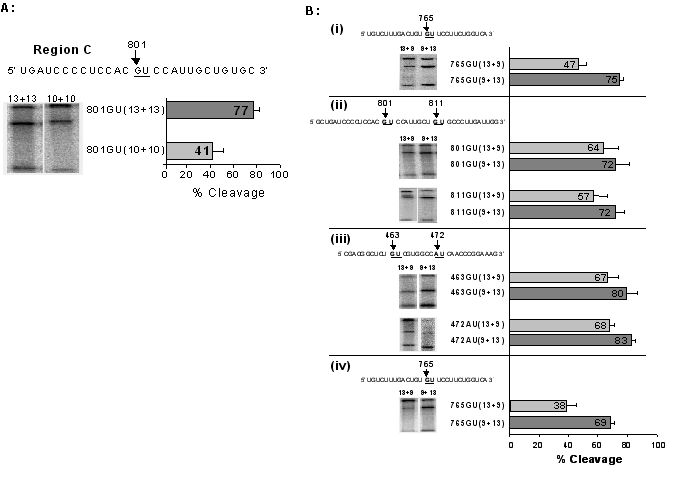
Binding arm length and asymmetric DNAzymes. (A) The 801GU cleavage site in region C was targeted by two DNAzymes with differing binding arm lengths (13+13 and 10+10) under simulated physiological conditions. Example autoradiographs of in vitro cleavage reactions for the 13+13 and 10+10 DNAzymes are shown. The cleavage efficiency after four hours, determined from four independent experiments in each case, is shown following quantification of 32P signals by phosphoimage analysis. (B) Pairs of asymmetrical DNAzymes with differing binding arm lengths were targeted at the five different cleavage sites using simulated physiological conditions. In each case example autoradiographs of in vitro cleavage reactions and the cleavage efficiency after four hours, determined from four independent experiments, are shown. (i) Cleavage of a short 459 nucleotide AChR α-subunit cRNA substrate at the 764GU site, by 764GU(13+9) and 764GU(9+13) DNAzymes. (ii) Cleavage of full-length α-subunit cRNA substrate at two cleavage sites 801GU and 811GU. (iii) Cleavage of full-length α-subunit cRNA substrate at two cleavage sites 463GU and 472AU. (iv) Cleavage of a full-length α-subunit cRNA substrate at the 764GU site at 10 mM Mg2+.
