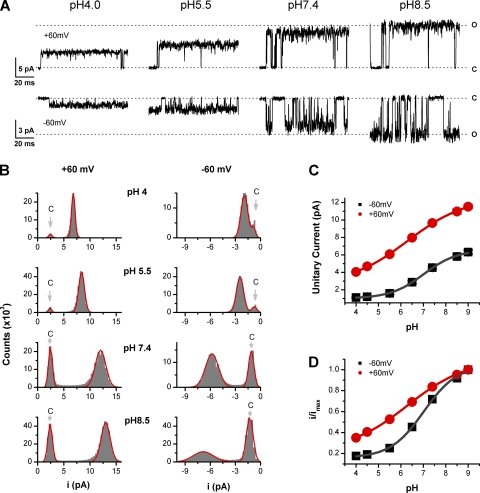
Figure 1.
Extracellular protons reduce single-channel conductance of TRPV1 channels. (A) Representative single-channel currents at the indicated pH recorded from an outside-out patch of oocyte membrane expressing TRPV1. The external and internal solutions were symmetrical 150 mM KCl. Recordings at two membrane potentials were shown (±60 mV) and were low-pass filtered at 2 kHz. (B) All-point amplitude histograms of single-channel currents. The histograms were fit to sums of two Gaussian functions to determine the closed and open amplitudes. The solid lines represent best fits. (C) Dose–response curves for the unitary current amplitudes obtained at ±60 mV versus the extracellular pH. The solid lines represent fits to the Hill equation with pKa ∼ 7, Hill coefficient of n ∼ 0.6 for Vh = −60 mV, and pKa ∼ 6 and n ∼ 0.3 for Vh = +60 mV, respectively. (D) Normalized dose–response relationships showing different dependence on pH at different membrane potentials (±60 mV).