Figure 1. Two photon excited fluorescence spectra of silk biomaterials.
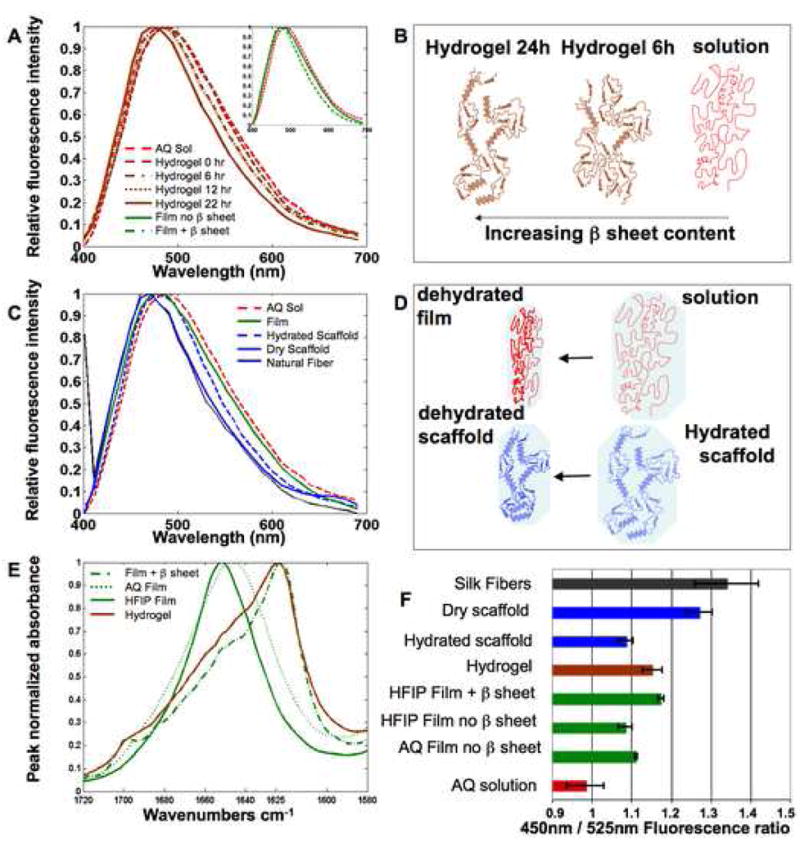
The spectral features of TPEF fluorescence resulting from 800 nm excitation of silk biomaterials are sensitive to silk II content and protein hydration. (A) The TPEF spectrum of an aqueous 8% silk solution becomes increasingly blue shifted during gelation induced by addition of HCL. Spectra at 6 and 12 hours of gelation overlap significantly. (A, Inset) A blue shift is also observed in the spectra of HFIP-processed films following b sheet induction by methanol treatment. (B) The main structural changes that are thought to contribute to the observed blue shift in panel (A) are depicted schematically. (C) A blue shift in the TPEF emission spectra is observed with decreased protein hydration. (D) The structural changes that are expected to accompany the level of exposure to a polar water environment are depicted for the transition from silk solution to silk film and from hydrated to dehydrated scaffold. (E) FTIR spectra reveal β sheet content. (F) Fluorescence intensity ratios of silk biomaterials.
