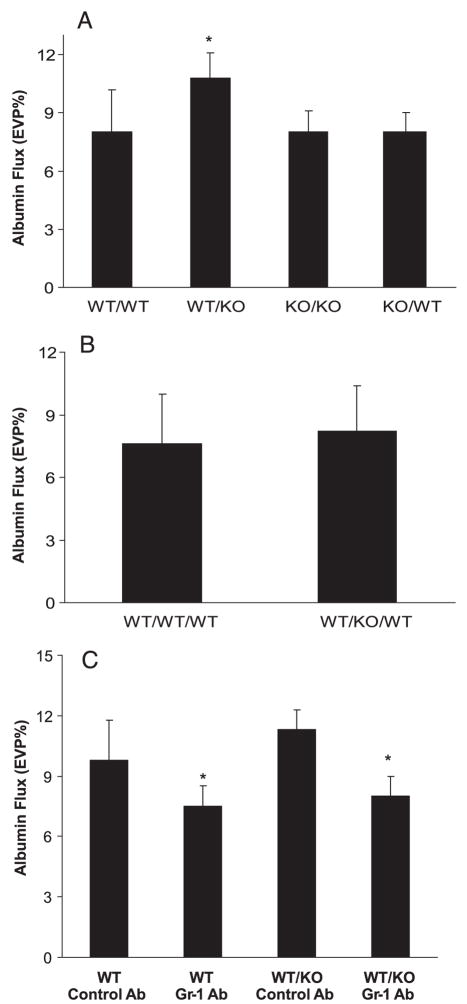
FIGURE 5.
Neutrophils and alveolar barrier protein permeability. A, WT mice lethally irradiated and reconstituted with bone marrow-derived hematopoietic cells from IL-6 null mice (WT/KO) had significantly higher lung albumin flux (expressed as EVP%) than WT mice reconstituted with WT bone marrow (WT/WT); *, p < 0.05, n = 8–9 in each group. KO/KO and KO/WT were similar to WT/WT mice. Therefore, the absence of IL-6 in hematopoietic cells only resulted in greater alveolar barrier disruption. B, Infusion of 106 WT bone marrow-derived neutrophils into WT/WT mice had no effect on lung protein permeability measured as albumin flux across the alveolar barrier compared with WT/WT mice. However, infusion of WT neutrophils into WT/KO mice resulted in a decrease in lung protein permeability to a level comparable to that of WT/WT mice. C, Depletion of neutrophils with Gr-1 Ab significantly decreased albumin flux in both WT and WT/KO mice. These data support a role for differences in neutrophil-mediated alveolar barrier dysfunction in the chimeric mice.