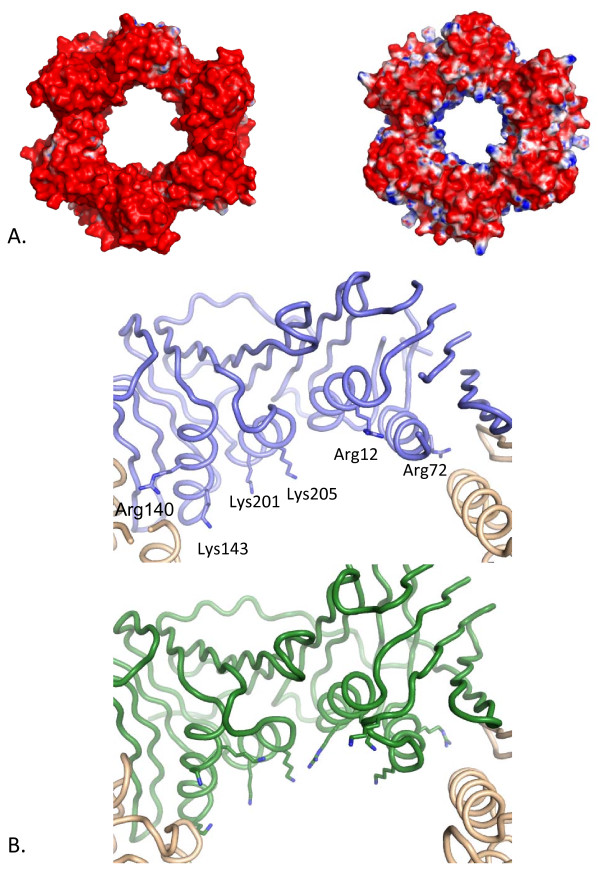
Figure 3.
Surface charge distribution of HvPCNA compared with AfPCNA. A. Electrostatic surfaces of Hv (left) and AfPCNA (right [PDB:1RWZ]) demonstrate that the acidic nature of PCNAs is more pronounced in HvPCNA and that the halophilic protein lacks the positive electrostatic charge characteristic of the inner channel. The electrostatic potential was calculated using the APBS package [43]. The accessible surface area is coloured according to the calculated electrostatic potential from -10 kBT/e (red) to +10 kBT/e (blue). B. Penetration of basic residues into the central channel of HvPCNA (top) and AfPCNA (bottom). The structures are depicted with a backbone trace with basic residues located on the α-helices lining the central pore depicted in stick representation. In HvPCNA only Lys143 and Lys205 project into the channel in the manner seen in classical PCNAs. Arg12, Arg72 and Arg140 are involved in substantial interactions with protein atoms and Lys201 is involved in charge neutralisation at the sodium cluster site. In contrast the majority of the basic residues lining the AfPCNA pore project into the channel.