Figure 2.
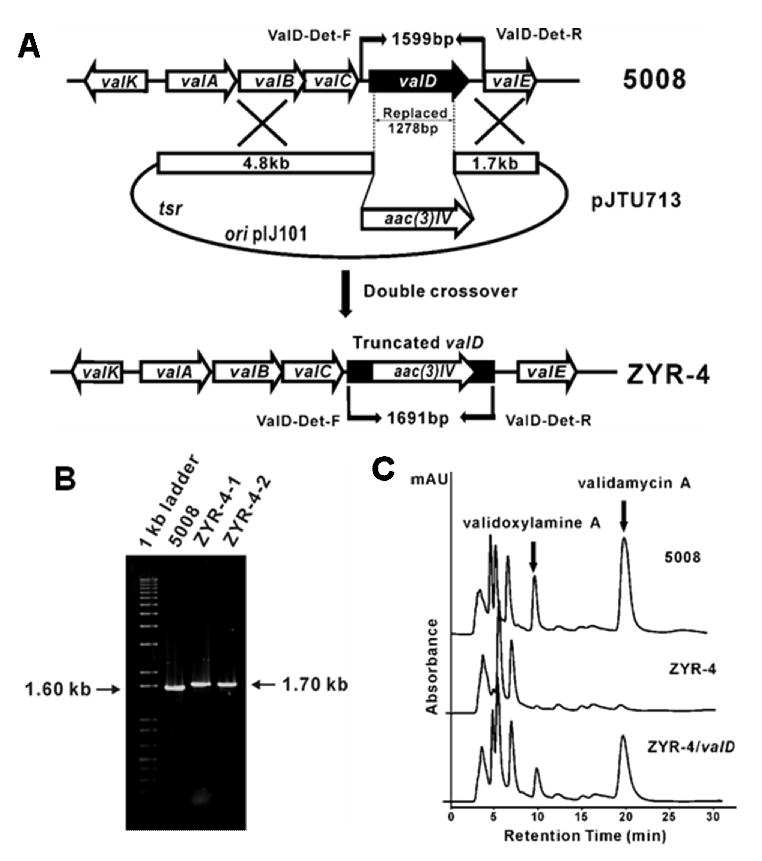
Construction and analysis of valD inactivated mutant strains of S. hygroscopicus 5008. A, Schematic representation for the replacement of a 1278-bp fragment of valD with apramycin resistance gene aac(3)IV. In shuttle plasmid pJTU713, aac(3)IV was inserted between 4.80-kb and 1.70-kb genomic fragments originally flanking the deleted 1278-bp region. While wild-type 5008 should give a 1.60-kb expected PCR-amplified product, mutant ZYR-4 should yield a 1.70-kb product using a pair of primers (ValD-Det-F and ValD-Det-R). B, Gel electrophoresis of PCR products of the wild-type and the mutant strains. C, HPLC analysis of the wild-type (5008), the valD mutant strain (ZYR-4), and the valD mutant strain complemented with a plasmid harboring an intact valD gene (ZYR-4/valD).Validamycin A and validoxylamine A are indicated with filled arrows.
