Figure 5.
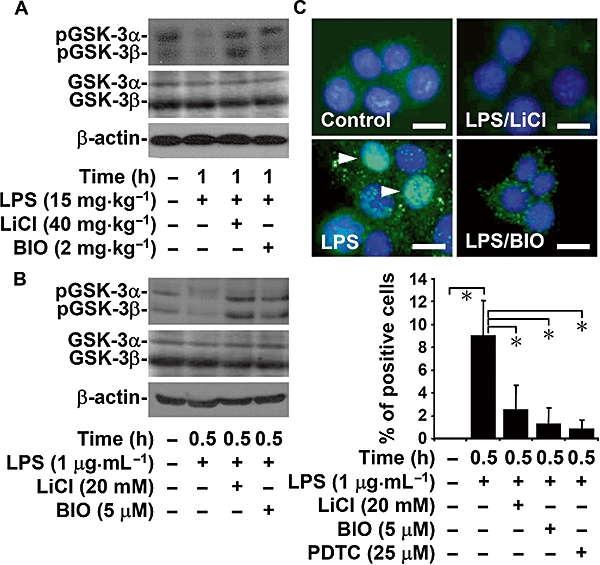
Inhibiting glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) blocked lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced GSK-3 and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation. C3H/HeN mice were injected with LPS (15 mg·kg−1 i.p.) for 1 h with or without lithium chloride (LiCl) (40 mg·kg−1) or 6-bromo-indirubin-3′-oxime (BIO) (2 mg·kg−1) co-treatment. M1 cells (3 × 106 cells/10 cm culture dish) were treated with LPS (1 µg·mL−1) for 0.5 h with or without LiCl (20 mM) or BIO (5 µM) pretreatment for 0.5 h. Western blot analysis was used to determine the phosphorylation of GSK-3α (Ser21) and GSK-3β (Ser9) in vivo (A) and in vitro (B). β-actin was the internal control. Data are representative of three mice or three individual experiments. (C) Fluorescent microscopy was used to determine the expression of NF-κB (green) in M1 cells immunostained with anti-NF-κB p65 antibody (positive cells: arrowheads). 4,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole was used for nuclei staining (blue). Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) (25 µM) was used as a positive control. Scale bar is 25 µm. Data obtained from three different areas are means ± SD *P < 0.05.
