Figure 2.
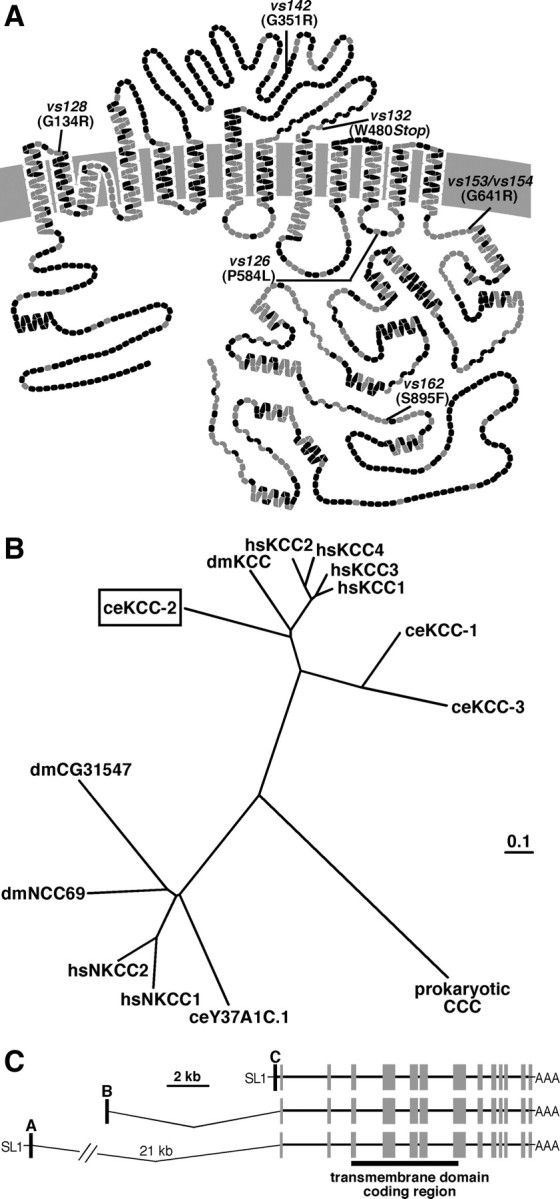
C. elegans KCC-2 exhibits sequence similarity to mammalian KCCs. A, Predicted transmembrane structure of C. elegans KCC-2 compared with the sequence of rat KCC2. Each amino acid is represented by a circle; gray circles indicate identical amino acids, and black circles represent non-identical amino acids. The locations of the kcc-2 mutations are as indicated. B, Phylogenetic comparison of C. elegans KCC-2 (ceKCC-2; boxed) to the four human KCCs (hsKCC1–hsKCC4), Drosophila melanogaster KCC (dmKCC), two additional C. elegans KCC homologs (ceKCC-1 and ceKCC-3), the human sodium potassium chloride cotransporters (hsNKCC1 and hsNKCC2), two predicted D. melanogaster NKCCs (dmCG31547 and dmNCC69), a predicted C. elegans NKCC (ceY37A1C.1), and a prokaryotic cation chloride cotransporter (CCC). C, Gene structure of C. elegans kcc-2. Three alternative splice forms, kcc-2a, kcc-2b, and kcc-2c, each contain a different 5′ exon (black boxes) that splices onto common exons (gray boxes) encoding the transmembrane domains (black bar). The SL1 trans splice leader (SL1) was identified on the A and C isoforms but not on the B isoform.
