Figure 4. 5-HT receptor binding is significantly lower in the arcuate nucleus of infants exposed to cigarette smoke prenatally.
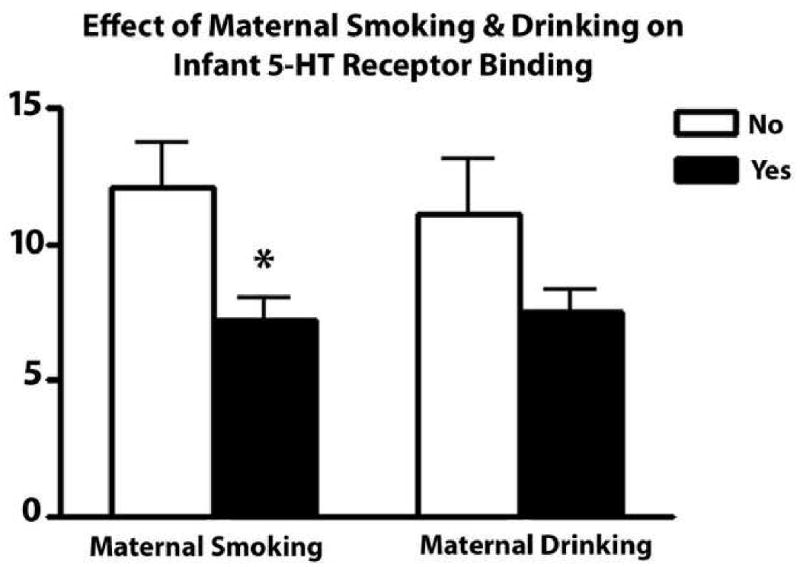
Graphs comparing the effects of prenatal smoking and prenatal alcohol on the effects of 5-HT receptor binding measured with 3H LSD autoradiography in the infant postnatally. Maternal smoking during pregnancy is associated with a 40% reduction (*p=0.011) and maternal alcohol ingestions during pregnancy is associated with a 32% reduction (p=0.075) in 5-HT receptor binding postnatally in infants.
