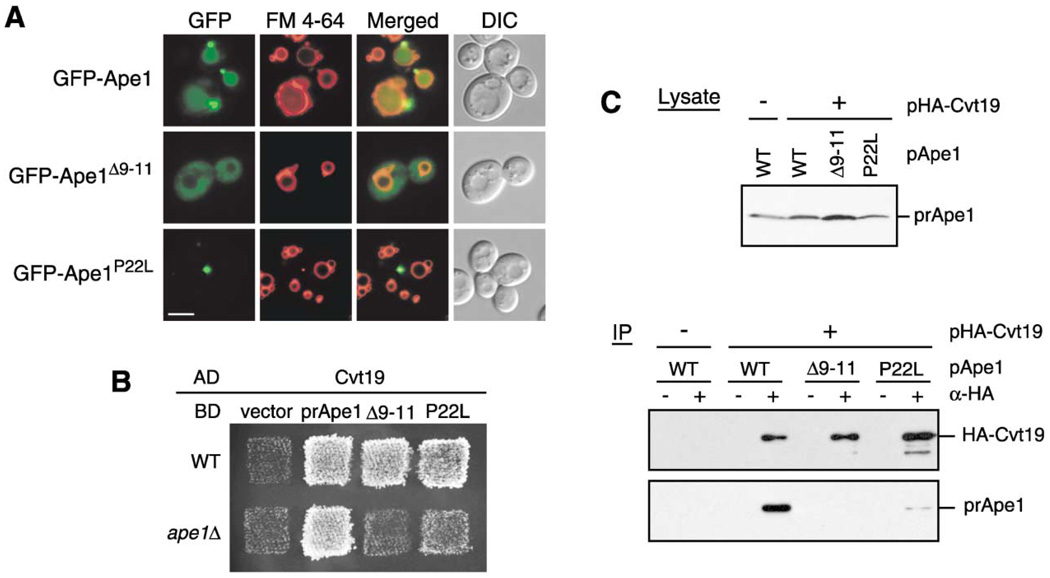
Figure 2. Precursor Ape1 Propeptide Is Required for the Formation of the Ape1 Complex and Interaction With Cvt19.
(A) Localization of the propeptide mutants of GFP-Ape1 by fluorescence and DIC microscopy. The ape1Δ cells harboring pGFP-Ape1, pGFP-Ape1Δ9–11, or pGFP-Ape1P22L were grown to midlog phase and labeled with FM 4-64 in SCD medium. Bar, 5 µm.
(B) Two-hybrid analysis of the physical interaction between Ape1 mutants and Cvt19. Wild-type (PJ69-4A) and isogenic ape1Δ (YTS110) test strains were transformed with the activation domain (AD) plasmid containing CVT19 and the binding domain (BD) plasmid containing wild-type or mutant APE1. Transformants were grown on an SC-Leu-Ura plate and replica plated on an SC-Ade-Leu-Ura plate to assess the interaction-dependent activation of the ADE2 gene. The cells shown here were grown at 30°C for 2 days.
(C) Interaction between prApe1 and Cvt19 is mediated by the prApe1 propeptide. Total lysate from the ape1Δ apg1Δ cells expressing HA-Cvt19 and either wild-type or mutant prApe1 from single-copy plasmids under the control of their own promoters were used for immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blot with anti-Ape1 and anti-HA antisera (IP). The top panel (Lysate) shows the protein blot of total cell lysate probed with anti-Ape1 antiserum.