Fig. 1.
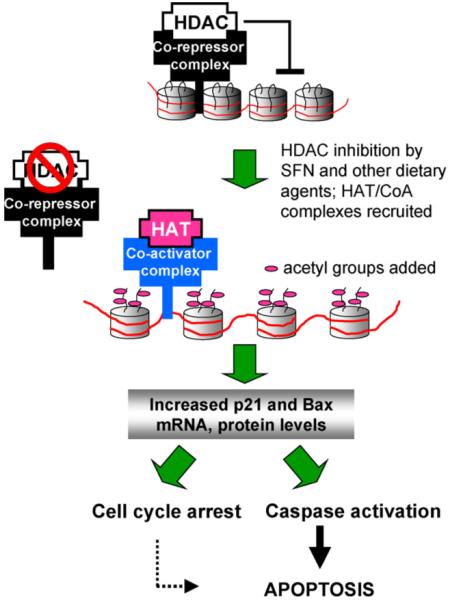
Working hypothesis for the role of dietary histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. HDAC/co-repressor complexes maintain a tightly restricted chromatin configuration, which limits access of transcription factors to DNA, and represses genes required for cell cycle checkpoint control and apoptosis. HDAC inhibition by SFN and other dietary agents enables histone acetyltransferase/co-activator (HAT/CoA) complexes to add acetyl groups to histone tails, loosening DNA/chromatin interactions, and allowing access of transcription factors to the promoters of genes such as P21 and bax. Re-expression of these genes facilitates cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in the context of cancer chemoprevention or therapy.
