Fig. 3.
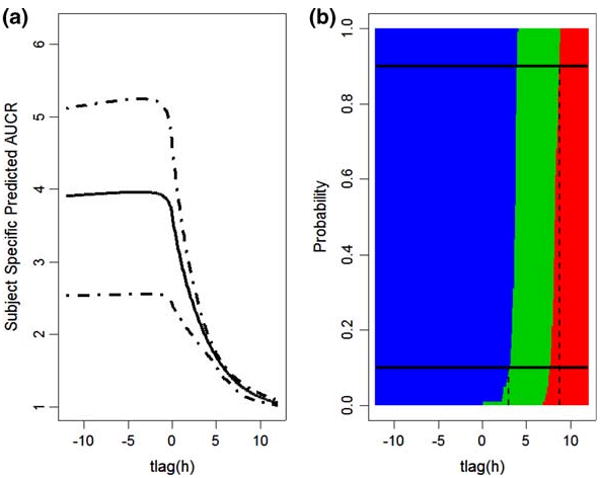
Effects of dosage separation on DDI when KETO(PO)/MDZ(IV) combination is 800/10 mg and Ki = 0.0037. a The mean and 90% credit intervals for AUCR predicted based on between-subject variability across the interval from −12 to 12 h. Negative values indicate that KETO is administrated before MDZ, and positive that MDZ administered prior to KETO. b The blue represents Pr{AUCRsubj > 2}, the green represents Pr{1.25 < AUCRsubj < 2}, the red represents Pr{AUCRsubj < 1.25}. The top black solid horizontal line represents the probability = 0.9, and it crosses the red region when the interval between administration is 8.8, indicating that if PO KETO is administrated 8.8 h after MDZ IV or later, the effect on AUCR will be clinically insignificant with probability larger that 90%. The black solid line at the bottom represents probability = 0.1, and it crosses the blue region when the time interval between dosage of interacting drugs is 3.0, meaning that if PO KETO is administrated within 3 h after MDZ IV, the inhibition will be clinically significant with probability larger that 90%. Otherwise, their DDI will be a weak interaction
