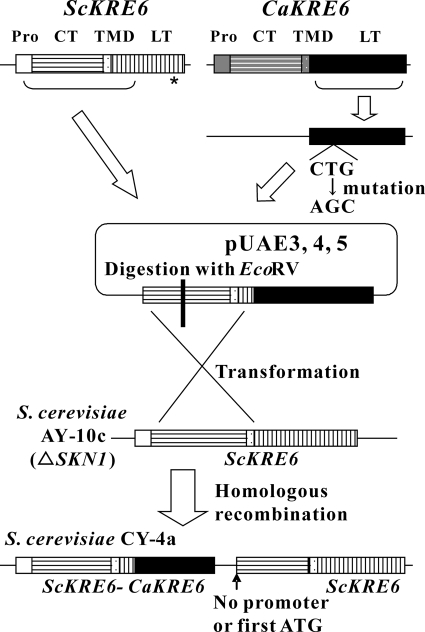
FIG. 2.
Schematic illustration for the construction of S. cerevisiae CY-4a. S. cerevisiae CY-4a, which expresses the fusion protein of ScKre6p and C. albicans Kre6p, was constructed to form S. cerevisiae AY-10c, an SKN1 null mutant, by the scheme shown here (see Materials and Methods for details of the construction). The gene encoding the C-terminal region of CaKRE6 was subcloned, and its CUG codon was changed into AGC by site-directed mutagenesis. It was fused with the gene encoding the N-terminal region of ScKRE6 without a promoter region. The resulting plasmid was digested within the region of ScKRE6 with EcoRV and was transformed into S. cerevisiae AY-10c, so that the gene encoding the C-terminal region of ScKRE6 in the host strain was replaced by CaKRE6, yielding S. cerevisiae CY-4a. S. cerevisiae CY-1a, CY-3a, and CY-5a, which express S. cerevisiae KRE6 (CY-1a) or the gene encoding the fusion protein of S. cerevisiae KRE6 and C. albicans SKN2 (CY-3a) or SKN1 (CY-5a), were constructed in similar ways. Abbreviations: Pro, promoter; CT, predicted cytoplasmic domain; TMD, predicted transmembrane domain; LT, predicted luminal/periplasmic domain.