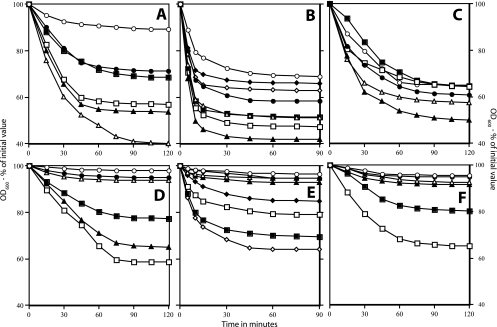
FIG. 1.
Germination of dormant and superdormant spores of Bacillus species following heat activation at different temperatures. Spores of Bacillus species were obtained, and superdormant spores were isolated following germination with inosine (B. cereus), glucose (B. megaterium) or l-valine (B. subtilis) as described in Materials and Methods. The dormant and superdormant spores were heat activated at various temperatures, cooled on ice, and germinated with the original germinants, and the OD600 of cultures was measured. The spores analyzed were B. cereus (A and D), B. megaterium (B and E), B. subtilis (C and F), original dormant (A, B, and C), and superdormant (D, E, and F). The symbols for the heat activation temperatures used in the various panels follow. Panels A and D: ○, no activation; •, 60°C; ▵, 65°C; ▴, 70°C; □, 75°C; ▪, 82.5°C. Panels B and E: ○, no activation; •, 50°C; ▵, 55°C; ▴, 60°C; □, 65°C; ▪, 70°C; ⋄, 75°C; ♦, 80°C. Panels C and F: ○, no activation; •, 65°C; ▵, 70°C; ▴, 75°C; □, 82.5°C; ▪, 87.5°C.