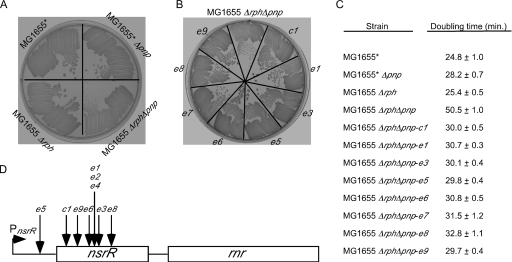
FIG. 1.
Growth of strains containing Δpnp and/or Δrph alleles and suppressors of the Δrph Δpnp growth defect. (A) MG1655* and derivatives containing Δpnp and/or Δrph alleles were streaked on an LB agar plate and incubated overnight at 37°C. (B) MG1655 Δrph Δpnp and eight distinct growth suppressors (see below) were streaked on an LB agar plate and grown at 37°C. Each suppressor is indicated by a different designation. Two suppressors (e2 and e4) were not streaked because they were found to harbor an insertion at the same location as e1. (C) Doubling times for MG1655*, derivatives containing Δpnp and/or Δrph alleles, and the MG1655 Δrph Δpnp suppressor strains determined in rich medium at 37°C. (D) Schematic diagram of the nsrR operon and transposon insertion sites for the MG1655 Δrph Δpnp suppressors. The nsrR gene and the downstream rnr coding regions are indicated by rectangles. The nsrR transcription start is indicated by a right-facing arrow, and the 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions flanking the nsrR coding region are indicated by a line. The location of each of mapped insertion site is indicated. The insertion sites in the 423-bp nsrR coding region are positions 31 (c1), 82 (e9), 147 (e6), 156 (e1, e2, and e4), 161 (e3), and 242 (e8). The e5 mutation maps to 32 bp upstream of the coding region. The insertion site for the e7 mutation could not be determined and hence is not shown.