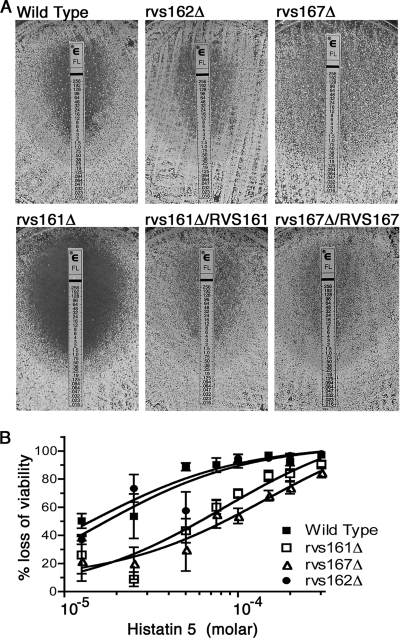
FIG. 6.
Altered responses of rvsΔ mutants to antifungal agents. (A) Increased susceptibility of rvs161Δ mutant to fluconazole. The indicated cells were spread onto solid RPMI medium, and then an Etest strip was applied to the agar surface to generate a gradient of fluconazole. rvs161Δ demonstrated increased susceptibility to fluconazole at 48 h, with no growth within the ellipse of inhibition, unlike the wild-type, rvs167Δ, or rvs162Δ strain or a strain in which rvs161Δ was complemented by the introduction of one copy of RVS161. Strains used were YLD14 (rvs161Δ), YLD22 (rvs162Δ), YLD16 (rvs167Δ), YLD11 (rvs161Δ/rvs161Δ/RVS161), and wild-type DIC185. (B) Cells were incubated at 37°C with the indicated concentration of Hst 5 for 90 min and then dilutions were plated to determine the loss of viability. rvs161Δ and rvs167Δ showed greater resistance to Hst 5 than either the wild-type or rvs162Δ strains at all concentrations tested. The half-maximal responses indicated a 5.9-fold resistance for rvs161Δ and a 10.3-fold resistance for rvs167Δ. Each data point represents the average of the results from three independent experiments. Bars indicate standard errors. Strains used were YLD14 (rvs161Δ), YLD22 (rvs162Δ), YLD16 (rvs167Δ), and wild-type DIC185.