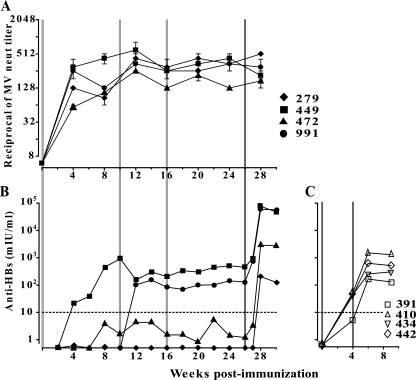
FIG. 3.
Humoral immune response against MV (A) or HBsAg (B and C) in rhesus monkeys immunized with MVvac2(HBsAg)N (A and B) or recombinant HBsAg protein vaccine (C). MV seronegative rhesus monkeys (A and B; ID in top panel) were housed at the California National Primate Research Center in accordance with the regulations of the Association for the Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care and were vaccinated subcutaneously with an MV vaccine-equivalent dose (104 TCID50) of MVvac2(HBsAg)N at day 1 and at 10 and 16 weeks afterwards (light-gray vertical lines) and with one dose of pediatric recombinant HBsAg protein vaccine (Engerix-B) at 26 weeks (dark-gray vertical line). Animals were monitored daily for MV-related symptoms. They were bled, under ketamine sedation, on days 0, 4, 7, and 14 and every 2 weeks thereafter. Measles viremia was quantified as previously described (18). (C) Rhesus monkeys were immunized with two doses of pediatric recombinant HBsAg protein vaccine at day 1 and 4 weeks afterwards (gray vertical lines). In panel A, averages and standard deviations of the results for at least four independent determinations are shown. In panels B and C, protective levels of anti-HBs (10 mIU/ml) are indicated by an interrupted line. Anti-HBs titers were determined by a quantitative automated anti-HBs assay (Vitros ECiQ Immunodiagnostic System, Ortho Clinical Diagnostics, Inc., Raritan, NJ). neut, neutralizing.