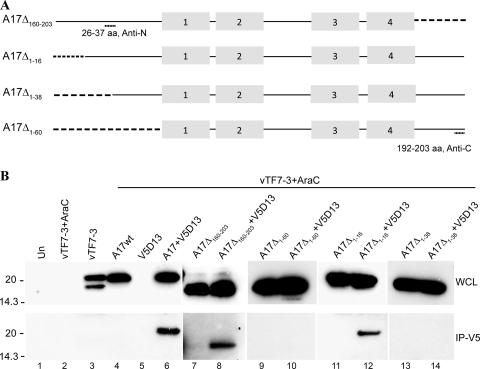
FIG. 3.
Effects of A17 truncations on interaction with D13. (A) Diagram of A17 truncation mutants. A17Δ160-203 has 44 amino acids deleted from the C terminus; A17Δ1-16, A17Δ1-38, and A17Δ1-60 have 16, 38, and 60 amino acids, respectively, deleted from the N terminus of A17. Truncations are indicated by dashed lines. Antibodies for Western blotting were raised against peptides corresponding to amino acids 26 to 37 (Anti-N) or 192 to 203 (Anti-C). The gray boxes indicate the four ∝-helical hydrophobic domains. (B) In the lanes under the bar, the samples were obtained from cells that were infected with vTF7-3 in the presence of AraC and transfected with plasmids encoding full-length (wild type) A17 (A17wt) or A17 truncation mutants alone or with V5-tagged D13 as indicated. In the lanes to the left of the bar, samples were from untransfected cells that were uninfected (Un), infected with vTF7-3 in the presence of AraC, or infected with vTF7-3 without AraC. After 24 h, the cells were lysed and subjected directly to SDS-PAGE (WCL) or first bound and then eluted from anti-V5-conjugated agarose beads (IP-V5). Western blotting was performed with rabbit anti-A17N (lanes 1 to 8) or anti-A17C (lanes 9 to 14) and developed by chemiluminescence. Molecular masses (kDa) are shown on the left.