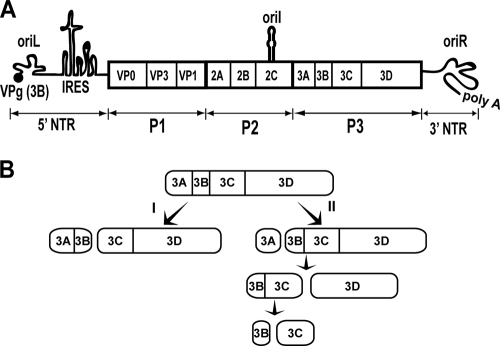
FIG. 1.
PV genome organization and P3 processing pathway. (A) Schematic of the PV genome. The 5′ end of the genome is covalently linked to a peptide (VPg) encoded by the 3B region of the genome. The 3′ end contains a poly(rA) tail. Three cis-acting replication elements are known. oriL is located in 5′ NTR. oriR is located in the 3′ NTR. oriI is located in 2C-coding sequence for PV; the position of this element is virus dependent. oriI is the template for VPg uridylylation. Translation initiation employs an internal ribosome entry site (IRES). The single open reading frame encodes a polyprotein. P1 produces virion structural proteins as indicated. P2 produces proteins thought to participate in virus-host interactions required for genome replication. P3 produces proteins thought to participate directly in genome replication. Polyprotein processing is mediated by protease activity residing in 2A, 3C, and/or 3CD proteins. (B) Processing of the P3 precursor occurs by two independent pathways (60). There are major (I) and minor (II) pathways. In pathway I, processing between 3B and 3C yields 3AB and 3CD. In pathway II, processing between 3A and 3B yields 3A and 3BCD. 3BCD processing yields 3BC and 3D; 3BC processing yields 3B and 3C. Pathway II is proposed to function in genome replication and is not perturbed in the GG mutant.