FIG. 2.
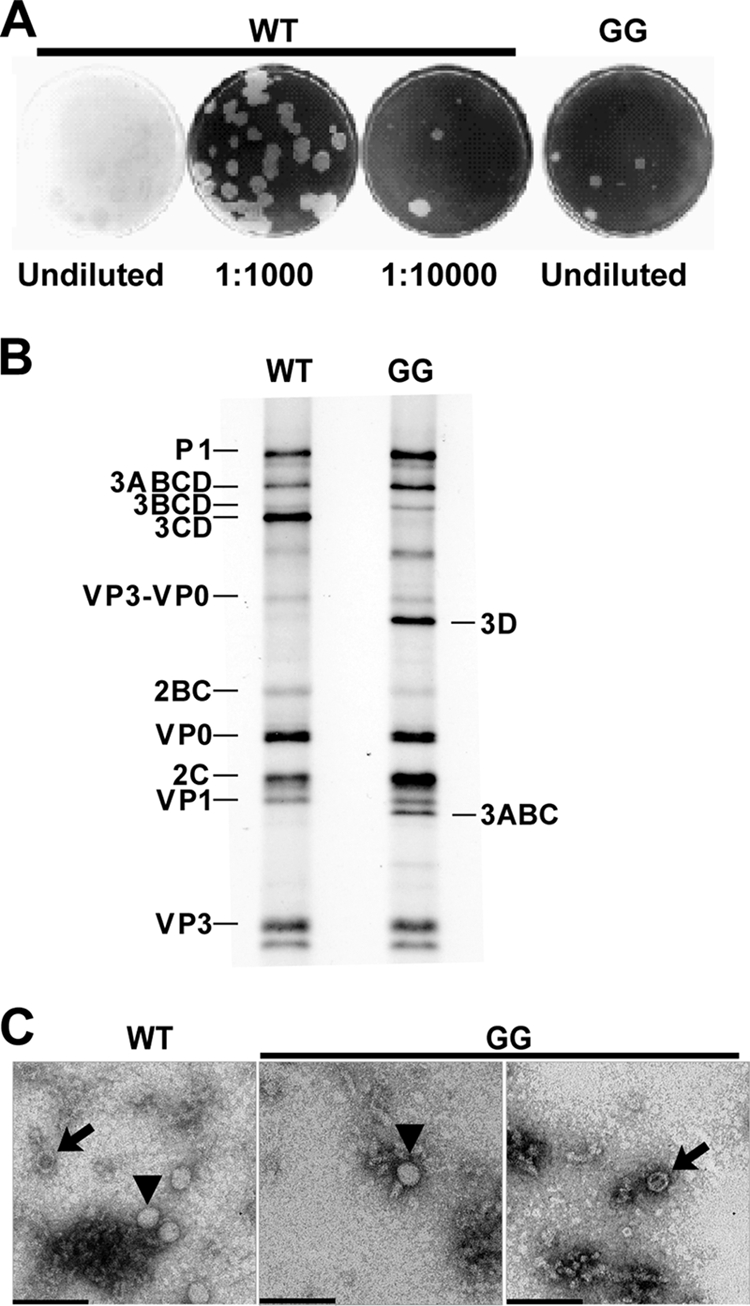
Changing the 3B-3C cleavage site from QG to GG produces a quasi-infectious virus. (A) Specific infectivity of GG mutant and WT PV RNA. HeLa cells were transfected with GG mutant or WT PV RNA, diluted, added to HeLa cell monolayers, overlaid with agarose, and held at 34°C for 5 days, at which time the agarose overlay was removed and cells were stained with crystal violet. From each of the five plaques obtained for the GG mutant RNA transfection, virus was plaque purified and viral RNA was extracted, reverse transcribed, and sequenced. Sequencing identified a single mutation at the 3B-3C cleavage site that converted GG to EG. (B) Processing evaluated by cell-free translation. HeLa cell-free translation extracts containing [35S]methionine and [35S]cysteine were programmed with WT or GG mutant RNA. Radiolabeled proteins were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE and detected by phosphorimaging. The bands corresponding to the different precursor and processed proteins expected for the WT are indicated on the left. The identities of bands unique to the GG mutant are indicated on the right. (C) TEM of WT and GG virus particles. HeLa cells were transfected with GG mutant or WT PV RNA and incubated at 34°C for 20 h, at which time cells were harvested and lysed with three freeze-thaw cycles. WT and GG mutant PV particles were then purified by precipitation using 10% PEG 8000 followed by centrifugation through a 30% sucrose cushion. Purified virus particles were negatively stained with 2% UA and observed by TEM. Bars = 0.1 μm. Representative virus particles that are empty (arrows) or contain packaged RNA (▾) are indicated.
