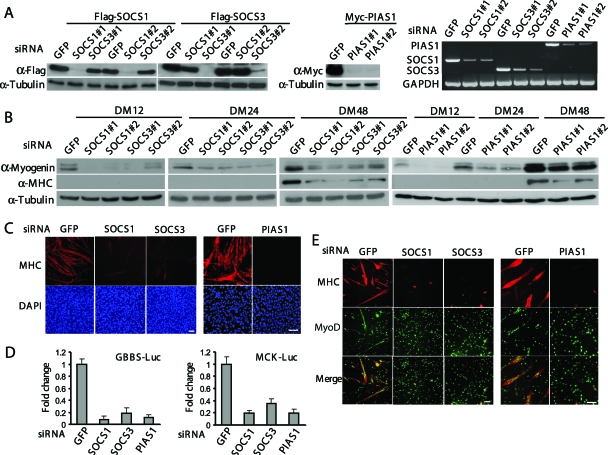
FIG. 2.
Individual knockdown of SOCS1, SOCS3, or PIAS1 genes inhibits differentiation both in primary myoblasts and C2C12 cells. (A) C2C12 cells were transfected with either siRNA alone or siRNA plus cDNA expression vectors as indicated. Cells were harvested 24 h after transfection. Either WCE or total RNA was prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis or RT-PCR. #1 and #2, different sets of siRNAs. (B and C) C2C12 cells were transfected with various siRNAs as indicated. (B) WCE was collected at different time points. Fifty micrograms of WCE was subjected to Western blot analysis with various antibodies. (C) Twenty-four hours after siRNA transfection, C2C12 cells were cultured in DM for another 48 h before being fixed and subjected to immunostaining with an anti-MHC antibody (MF20). The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Bars, 100 μm. (D) C2C12 cells were cotransfected with siRNA and luciferase reporter constructs in different combinations as indicated. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were allowed to grow in DM for another 24 h (for GBBS-Luc) or 48 h (for MCK-Luc) before being harvested. WCE was collected and subjected to luciferase assays. All the samples were prepared in triplicate, and the results are presented as the mean ± the standard deviation (error bars). The change was calculated as the ratio of the luciferase activity in SOCS (or PIAS)-siRNA-transfected cells to that in GFP-siRNA-transfected cells. (E) Freshly isolated primary myoblasts were separately transfected with SOCS1-, SOCS3-, or PIAS1-siRNA. Cells were fixed after 24 h in DM and subjected to double immunostaining with anti-MyoD and anti-MHC antibodies. Bars, 100 μm.