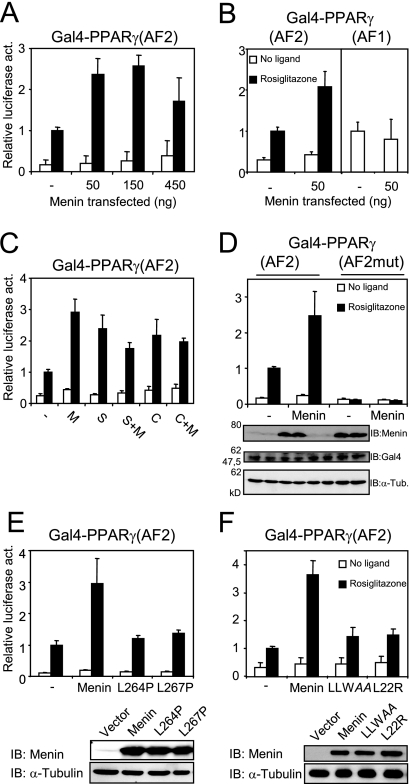
FIG. 7.
Menin coactivates PPARγ-mediated transcription in a ligand-dependent fashion. (A) Cos7 cells were transiently transfected with a 5× GalTK-luciferase construct and an expression plasmid for Gal4-PPARγ(AF2) and treated with 1 μM rosiglitazone or DMSO for 24 h. Increasing amounts of menin were cotransfected. Firefly luciferase readings were normalized against Renilla luciferase, which served as an internal control. Columns represent averages and standard deviations of two independent experiments performed in triplicate. All luciferase assays shown were performed in this fashion. (B) Menin was overexpressed in cells cotransfected with Gal4-PPARγ(AF2) and in cells coexpressing Gal4-PPARγ(AF1). (C) Along with 50 ng of the menin (M) expression plasmid, cells were transfected with 450 ng of pSG5-SRC1e (S), 450 ng pSG5-HA-CARM1 (C), or a combination of these factors and menin. (D) A Gal4-PPARγ(AF2) construct bearing two mutations in helix 12 (L468A E471A) was transiently transfected into Cos7 cells. Protein levels of menin, Gal4-PPARγ(AF2), and α-tubulin (α-Tub.) were determined by immunoblotting (IB). Lanes on the gel correspond to the columns shown in the panel above. (E) Expression plasmids encoding the L264P and L267P menin mutants were cotransfected with Gal4-PPARγ(AF2). Menin protein levels were determined by immunoblotting with α-tubulin as a loading control. (F) The LLWAA and L22R mutations were also introduced in the MEN1 expression plasmid and transfected into Cos7 cells for luciferase assays. Protein levels were determined as in panel E.