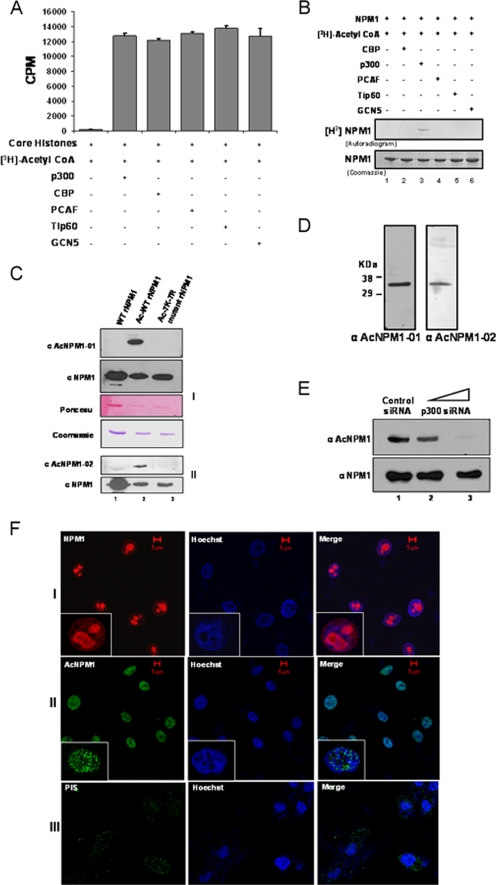
FIG. 1.
p300 acetylates NPM1 in the nucleoplasm. (A) Results of a filter binding assay performed to normalize the activities of different HATs with core histones (purified from HeLa cells) as substrates are represented as bar graphs. CoA, coenzyme A. (B) An in vitro HAT assay was performed with 1 μg recombinant NPM1 (rNPM1) as a substrate for different acetyltransferases. (C) Characterization of polyclonal antibodies raised against two acetylated NPM1 peptides, AcNPM1-01 (panel 1) and AcNPM1-02 (panel 2), by Western blotting along with the corresponding NPM1 control. The loading control of the proteins is also shown by Ponceau staining of the membrane, and the same amount of each protein was resolved separately and visualized by Coomassie staining. WT recombinant NPM1 (lane 1), in vitro acetylated WT recombinant NPM1 (lane 2), and 7K-7R mutant recombinant NPM1 were subjected to an in vitro acetylation reaction (lane 3). (D) HEK293T whole-cell extract was subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-AcNPM1-01 and anti-AcNPM1-02 antibodies. (E) Western blot analysis was done with anti-AcNPM1 antibody at 48 h posttransfection of p300 siRNA (upper panel). A corresponding loading control was done with anti-NPM1 antibody (lower panel). (F) Immunofluorescence staining of NPM1 (red) in HEK293T cells with anti-NPM1 monoclonal antibody (panel I) and acetylated NPM1 (green) with an anti-AcNPM1-01 polyclonal antibody (panel II). Rabbit PIS was used as a negative control for anti-Ac-NPM1-01 staining (panel III). DNA staining (blue) was done with Hoechst. Scale bar, 5 μm.