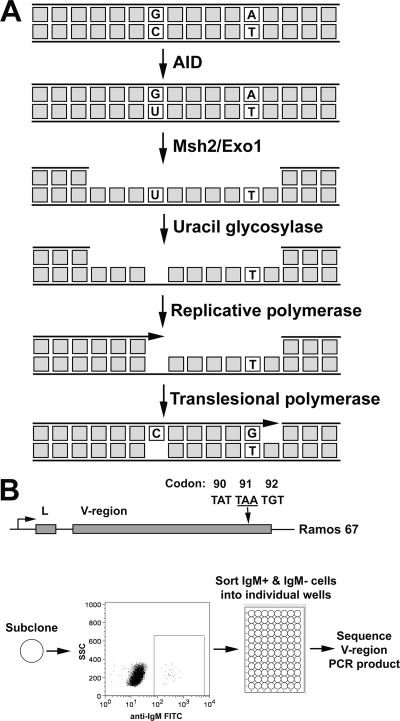
FIG. 1.
Model for mutagenic repair by MutSα. (A) A cytidine in the representative DNA sequence is deaminated by AID, thus generating a G·U lesion, which stimulates the MMR-directed Exo1 excision of the unmutated DNA strand. This yields a U in the opposite strand within an ssDNA region. The removal of the U by UNG generates an abasic site. The resynthesis of the excised strand begins with an error-free replicative polymerase until the abasic site is encountered, causing the polymerase to stall. This leads to translesional synthesis, with the recruitment of error-prone polymerases to bypass the abasic site as well as polymerase η to generate mutations at A·T base pairs. (B) On the top is a schematic of the IgH locus of Ramos 67 (R67) cells with the position of the TAA nonsense codon represented by an arrow. On the bottom is a diagram describing the enrichment for Ramos clones containing A·T mutations, including subcloning, sorting based on IgM expression, and the sequencing of the V region. FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate.