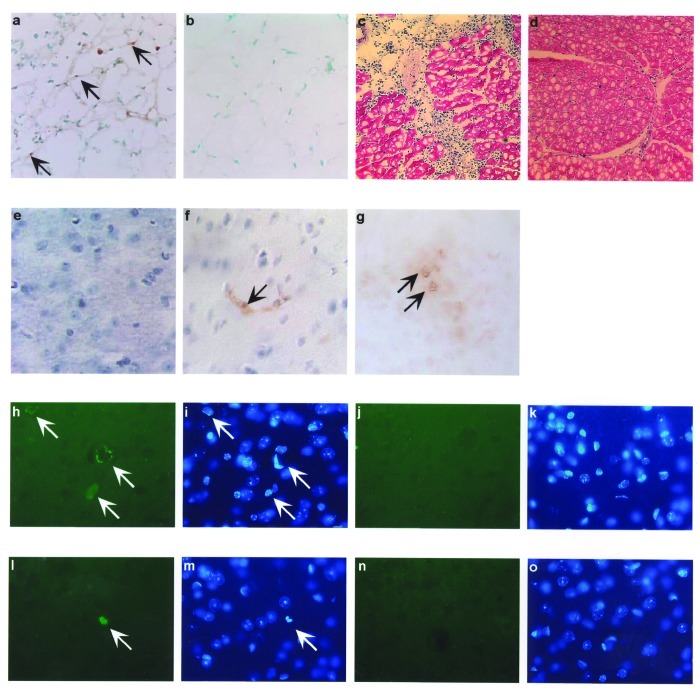
Figure 3.
In vivo West Nile virus capsid (Cp) expression induces apoptosis and inflammation in mice. TUNEL assay was performed on muscle cryosections harvested from mice injected with pcWNV-Cp-DJY (a) or pcDNA3.1 (b). Hematoxylin/eosin staining was performed on mouse tibialis muscle cryosections harvested from mice injected with pcWNV-Cp-DJY (c) or pcDNA3.1 (d) at 48 h postinjection (magnification: 200X [a, b] and 40X [c,d]). Immunohistochemical analysis was performed for detection of WNVCp-DJY protein expression in mouse brain injected with pcDNA3.1 or pcWNV-Cp-DJY as detected with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) (e,f, respectively). TUNEL assay on mouse brain cryosections harvested from pcWNV-Cp-DJY injected mouse was detected with HRP (g) (magnification: 300X [e–g]). Immunohistochemical studies were performed for detection of WNV-Cp-DJY protein expression in mouse brain injected with pcWNV-Cp-DJY or pcDNA3.1 as detected by fluorescein isothiocynate stain (h, i, and j, k, respectively). TUNEL assay on mouse brain cryosections harvested from pcWNV-Cp-DJY–injected mice (l,m) or pcDNA3.1-injected mice as detected with fluorescein isothiocyanate (n,o). WNV-Cp-DJY protein expressing His-positive cells or TUNEL-positive cells were visualized under ultraviolete microscope (h or l, respectively). Nuclear staining for WNV-Cp-DJY– or pcNDA3.1-transfected cells was visualized with appropriate filters (i, m or k, o, respectively) (magnification: 630X [h through o]).