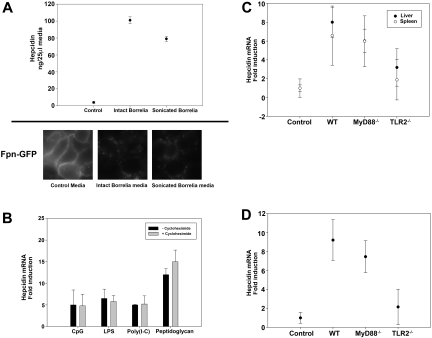
Figure 4.
Hepcidin secretion by bone marrow macrophages stimulated with B burgdorferi is TLR2 dependent. (A) Bone marrow macrophages from C3H mice stimulated with either intact or sonicated B burgdorferi were analyzed for hepcidin production. Media from cultured macrophages was analyzed for hepcidin 24 hours after incubation. HEK 293T cells expressing Fpn-GFP were incubated with media used to culture WT macrophages infected with intact or sonicated B burgdorferi. Ferroportin degradation was analyzed by epifluorescence microscopy. (B) Bone marrow macrophages from C3H mice were stimulated with TLR-specific agonists (20 μg/mL CpG, TLR9 agonist; 10 ng/mL LPS, TLR4 agonist; 20 μg/mL Poly(I-C), TLR3 agonist; 20 μg/mL peptidoglycan, TLR2 agonist) in the presence or absence of cycloheximide (7.5 μg/mL). RNA was isolated and purified, and hepcidin and actin transcripts were analyzed by RT-PCR. (C) C57BL/6 uninfected (Control) and infected (WT), MyD88−/−, and TLR2−/− mice were sacrificed after 4 weeks of infection. RNA was isolated and purified from the livers and spleens, and hepcidin and actin transcripts were analyzed by RT-PCR. (D) Bone marrow macrophages from C57BL/6 control, WT, MyD88−/−, and TLR2−/− mice were stimulated with sonicated B burgdorferi. RNA was isolated and purified, and hepcidin and actin transcripts were analyzed by RT-PCR.