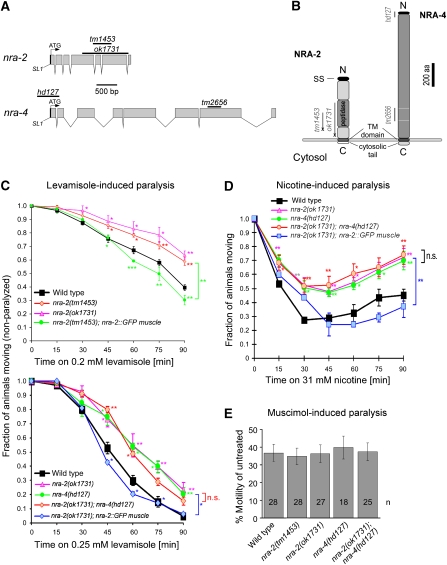
Figure 1.
Cholinergic agonist-induced phenotypes are altered in nra-2 and nra-4 mutants, and rescued by muscle-specific expression. (A) The nra-2 and nra-4 genes, as annotated in www.wormbase.org, were confirmed by sequencing cDNAs kindly provided by Y Kohara. Sequences deleted in the alleles used are indicated by bars. (B) The nra-2 and nra-4 genes encode predicted type I TM proteins with signal sequences (SS), thus they are expected to be synthesized into the ER lumen, exposing a short C-terminal cytosolic tail. Deletion/insertion alleles tm1453 and ok1731 truncate NRA-2, bringing stop codons (X) in frame. nra-4(hd127) removes part of the promoter and exon I including SS and start codon and tm2656 is a predicted in-frame deletion. (C, D) Paralysis time-course of wild-type and mutant animals exposed to 0.2 or 0.25 mM levamisole (C) or 31 mM nicotine (D). The fraction of non-paralyzed animals was counted every 15 min. Experiments were repeated 3–7 times (30 animals tested each time), data represent mean±s.e.m., statistically significant differences to wild type are indicated (*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001). Brackets indicate overall significant differences between genotypes, if they were different for at least three time points. (E) Swimming cycles of animals immersed for 1 h in M9 buffer with 8 mM muscimol, a GABAAR agonist, were normalized to swimming cycles of untreated control animals.